Urinary L-type fatty acid-binding protein can reflect renal tubulointerstitial injury
- PMID: 19264908
- PMCID: PMC2671353
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2009.080511
Urinary L-type fatty acid-binding protein can reflect renal tubulointerstitial injury
Abstract
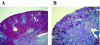
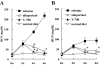
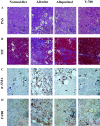
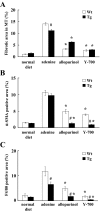
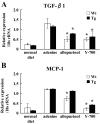
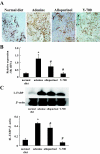
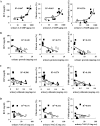
This study aimed to elucidate the role of L-type fatty acid-binding protein (L-FABP) in renal tubulointerstitial injury using a mouse adenine-induced renal injury model. C57BL/6 mice fed excess dietary adenine for 6 weeks showed a gradual increase in levels of blood urea nitrogen (BUN). They also showed severe tubulointerstitial pathological findings, such as fibrosis and macrophage infiltration without glomerular damage, which were attenuated by treatment with either allopurinol or Y-700, a new xanthine dehydroxygenase inhibitor. Because renal expression of L-FABP is defective in C57BL/6 mice, human L-FABP transgenic mice were fed an adenine-containing diet. Transgenic mice showed lower BUN levels and lower levels of pathological injury compared with wild-type mice. On the other hand, urinary levels and renal expression of L-FABP in the adenine group was significantly increased and attenuated by treatment with either allopurinol or Y-700. Urinary L-FABP was positively correlated with BUN levels and pathological damages in the tubulointerstitium. No increases in urinary protein, albumin, or N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminidase levels were found for 6 weeks in any group. In conclusion, we demonstrated that urinary L-FABP levels can be used to monitor both dynamics and drug responses in a mouse adenine-induced tubulointerstitial injury model.
Figures
References
-
- Sarnak MJ, Levey AS, Schoolwerth AC, Coresh J, Culleton B, Hamm LL, McCullough PA, Kasiske BL, Kelepouris E, Klag MJ, Parfrey P, Pfeffer M, Raij L, Spinosa DJ, Wilson PW. Kidney disease as a risk factor for development of cardiovascular disease: a statement from the American Heart Association Councils on Kidney in Cardiovascular Disease, High Blood Pressure Research, Clinical Cardiology, and Epidemiology and Prevention. Circulation. 2003;108:2154–2169. - PubMed
-
- Risdon RA, Sloper JC, De Wardener HE. Relationship between renal function and histological changes found in renal-biopsy specimens from patients with persistent glomerular nephritis. Lancet. 1968;2:363–366. - PubMed
-
- Mackensen-Haen S, Bader R, Grund KE, Bohle A. Correlations between renal cortical interstitial fibrosis, atrophy of the proximal tubules and impairment of the glomerular filtration rate. Clin Nephrol. 1981;15:167–171. - PubMed
-
- Nath KA. Tubulointerstitial changes as a major determinant in the progression of renal damage. Am J Kidney Dis. 1992;20:1–17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

