Membrane type-1 matrix metalloproteinase potentiates basic fibroblast growth factor-induced corneal neovascularization
- PMID: 19264910
- PMCID: PMC2671386
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2009.080452
Membrane type-1 matrix metalloproteinase potentiates basic fibroblast growth factor-induced corneal neovascularization
Erratum in
- Am J Pathol. 2013 Jul;183(1):326
Abstract
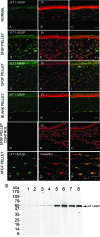
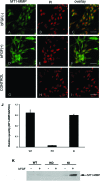
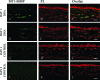
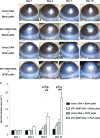
Corneal neovascularization is one of the leading causes of blindness. The aim of this study was to evaluate the pro-angiogenic role of corneal fibroblast-derived membrane type-1 matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP) on basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF)-induced corneal neovascularization in vivo and in vitro. Immunohistochemical studies demonstrated that MT1-MMP was expressed in keratocytes and immortalized corneal fibroblast cell lines. Vascular endothelial growth factor protein levels were increased after bFGF-stimulation of wild-type fibroblast cells compared with MT1-MMP knockout fibroblast cells. Corneal vascularization was significantly increased after a combination of bFGF pellet implantation and naked MT1-MMP DNA injection in wild-type mouse corneas compared with either bFGF pellet implantation or naked MT1-MMP DNA-injected corneas. Western blotting analysis of the phosphorylation levels of the key signaling molecules (p38, JNK, and ERK) demonstrated that phosphorylation levels of both p38 and JNK were diminished after bFGF stimulation of MT1-MMP knockout cells compared with wild-type and MT1-MMP knockin cells. These results suggest that MT1-MMP potentiates bFGF-induced corneal neovascularization, likely by modulating the bFGF signal transduction pathway.
Figures
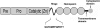
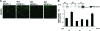

References
-
- Tallquist MD, Soriano P, Klinghoffer RA. Growth factor signaling pathways in vascular development. Oncogene. 1999;18:7917–7932. - PubMed
-
- Yancopoulos GD, Davis S, Gale NW, Rudge JS, Wiegand SJ, Holash J. Vascular-specific growth factors and blood vessel formation. Nature. 2000;407:242–248. - PubMed
-
- Gale NW, Yancopoulos GD. Growth factors acting via endothelial cell-specific receptor tyrosine kinases: VEGFs, angiopoietins, and ephrins in vascular development. Genes Dev. 1999;13:1055–1066. - PubMed
-
- Kwon YS, Kim JC. Inhibition of corneal neovascularization by rapamycin. Exp Mol Med. 2006;38:173–179. - PubMed
-
- Kenyon BM, Voest EE, Chen CC, Flynn E, Folkman J, D'Amato RJ. A model of angiogenesis in the mouse cornea. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1996;37:1625–1632. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

