Ets transcription factors control epithelial maturation and transit and crypt-villus morphogenesis in the mammalian intestine
- PMID: 19264912
- PMCID: PMC2671360
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2009.080409
Ets transcription factors control epithelial maturation and transit and crypt-villus morphogenesis in the mammalian intestine
Abstract
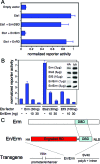
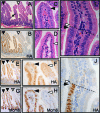
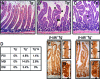
Members of the Ets transcription factor family are widely expressed in both the developing and mature mammalian intestine, but their biological functions remain primarily uncharacterized. We used a dominant repressor transgene approach to probe the function of epithelial Ets factors in the homeostasis of the crypt-villus unit, the functional unit of the small intestine. We show that targeted expression in small intestinal epithelium of a fusion protein composed of the Engrailed repressor domain and the Erm DNA-binding domain (En/Erm) results in marked disruption of normal crypt-villus homeostasis, including a cell-autonomous disturbance of epithelial maturation, increased epithelial transit, severe villus dysmorphogenesis, and crypt dysmorphogenesis. The epithelial maturation disturbance is independent of the regulation of TGFbetaRII levels, in contrast to Ets-mediated epithelial differentiation during development; rather, regulation of Cdx2 expression may play a role. The villus dysmorphogenesis is independent of alterations in the crypt-villus boundary and inappropriate beta-catenin activation, and thus appears to represent a new mechanism controlling villus architectural organization. An Analysis of animals mosaic for En/Erm expression suggests that crypt nonautonomous mechanisms underlie the crypt dysmorphogenesis phenotype. Our studies thus uncover novel Ets-regulated pathways of intestinal homeostasis in vivo. Interestingly, the overall En/Erm phenotype of disturbed crypt-villus homeostasis is consistent with recently identified Ets function(s) in the restriction of intestinal epithelial tumorigenesis.
Figures





References
-
- Oikawa T, Yamada T. Molecular biology of the Ets family of transcription factors. Gene. 2003;303:11–34. - PubMed
-
- Sharrocks AD. The ET: S-domain transcription factor family. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2001;2:827–837. - PubMed
-
- Gutierrez-Hartmann A, Duval DL, Bradford AP. ETS transcription factors in endocrine systems. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2007;18:150–158. - PubMed
-
- Graves BJ, Petersen JM. Specificity within the ets family of transcription factors. Adv Cancer Res. 1998;75:1–55. - PubMed
-
- Sementchenko VI, Watson DK. Ets target genes: past, present and future. Oncogene. 2000;19:6533–6548. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

