Identification of the phosphorylation sites on the E3 ubiquitin ligase Pellino that are critical for activation by IRAK1 and IRAK4
- PMID: 19264966
- PMCID: PMC2651833
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0900774106
Identification of the phosphorylation sites on the E3 ubiquitin ligase Pellino that are critical for activation by IRAK1 and IRAK4
Abstract
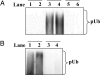
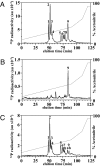
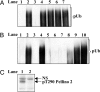
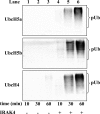
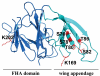
The E3 ubiquitin ligase Pellino can be activated by phosphorylation in vitro, catalyzed by IL-1 receptor-associated kinase 1 (IRAK1) or IRAK4. Here, we show that phosphorylation enhances the E3 ligase activity of Pellino 1 similarly with any of several E2-conjugating enzymes (Ubc13-Uev1a, UbcH4, or UbcH5a/5b) and identify 7 amino acid residues in Pellino 1 whose phosphorylation is critical for activation. Five of these sites are clustered between residues 76 and 86 (Ser-76, Ser-78, Thr-80, Ser-82, and Thr-86) and decorate a region of antiparallel beta-sheet, termed the "wing," which is an appendage of the forkhead-associated domain that is thought to interact with IRAK1. The other 2 sites are located at Thr-288 and Ser-293, just N-terminal to the RING-like domain that carries the E3 ligase activity. Unusually, the full activation of Pellino 1 can be achieved by phosphorylating any one of several different sites (Ser-76, Thr-86, Thr-288, or Ser-293) or a combination of other sites (Ser-78, Thr-80, and Ser-82). These observations imply that dephosphorylation of multiple sites is required to inactivate Pellino 1, which could be a device for prolonging Pellino's E3 ubiquitin ligase activity in vivo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Muzio M, Ni J, Feng P, Dixit VM. IRAK (Pelle) family member IRAK-2 and MyD88 as proximal mediators of IL-1 signaling. Science. 1997;278:1612–1615. - PubMed
-
- Wesche H, Henzel WJ, Shillinglaw W, Li S, Cao Z. MyD88: An adapter that recruits IRAK to the IL-1 receptor complex. Immunity. 1997;7:837–847. - PubMed
-
- Martin M, Bol GF, Eriksson A, Resch K, Brigelius-Flohe R. Interleukin-1-induced activation of a protein kinase coprecipitating with the type I interleukin-1 receptor in T cells. Eur J Immunol. 1994;24:1566–1571. - PubMed
-
- Kollewe C, et al. Sequential autophosphorylation steps in the interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase-1 regulate its availability as an adapter in interleukin-1 signaling. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:5227–5236. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

