Cutting edge: the PTPN22 allelic variant associated with autoimmunity impairs B cell signaling
- PMID: 19265110
- PMCID: PMC2797545
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.0713370
Cutting edge: the PTPN22 allelic variant associated with autoimmunity impairs B cell signaling
Abstract
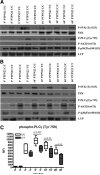
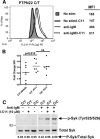
PTPN22 is a gene encoding the protein tyrosine phosphatase Lyp. A missense mutation changing residue 1858 from cytosine to thymidine (1858C/T) is associated with multiple autoimmune disorders. Studies have demonstrated that Lyp has an inhibitory effect on TCR signaling; however, the presence of autoantibodies in all of the diseases associated with the 1858T variant and recent evidence that Ca(2+) flux is altered in B cells of 1858T carriers indicate a role for Lyp in B cell signaling. In this study we show that B cell signal transduction is impaired in individuals who express the variant. This defect in signaling is characterized by a deficit in proliferation, a decrease in phosphorylation of key signaling proteins, and is reversed by inhibition of Lyp. These findings suggest that the PTPN22 1858T variant alters BCR signaling and implicate B cells in the mechanism by which the PTPN22 1858T variant contributes to autoimmunity.
Figures

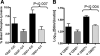
Similar articles
-
Altered B cell homeostasis is associated with type I diabetes and carriers of the PTPN22 allelic variant.J Immunol. 2012 Jan 1;188(1):487-96. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1102176. Epub 2011 Nov 21. J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22105996 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Overexpression of the PTPN22 Autoimmune Risk Variant LYP-620W Fails to Restrain Human CD4+ T Cell Activation.J Immunol. 2021 Aug 1;207(3):849-859. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2000708. Epub 2021 Jul 23. J Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34301848 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic variation in PTPN22 corresponds to altered function of T and B lymphocytes.J Immunol. 2007 Oct 1;179(7):4704-10. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.179.7.4704. J Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17878369
-
The putative role of the C1858T polymorphism of protein tyrosine phosphatase PTPN22 gene in autoimmunity.Autoimmun Rev. 2013 May;12(7):717-25. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2012.12.003. Epub 2012 Dec 20. Autoimmun Rev. 2013. PMID: 23261816 Review.
-
The role of PTPN22 risk variant in the development of autoimmunity: finding common ground between mouse and human.J Immunol. 2015 Apr 1;194(7):2977-84. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1403034. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25795788 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Autoimmunity-associated protein tyrosine phosphatase PEP negatively regulates IFN-α receptor signaling.J Exp Med. 2015 Jun 29;212(7):1081-93. doi: 10.1084/jem.20142130. Epub 2015 Jun 15. J Exp Med. 2015. PMID: 26077719 Free PMC article.
-
The Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase Nonreceptor 22 (PTPN22) R620W Functional Polymorphism in Psoriasis.Clin Med Insights Arthritis Musculoskelet Disord. 2018 Jan 11;11:1179544117751434. doi: 10.1177/1179544117751434. eCollection 2018. Clin Med Insights Arthritis Musculoskelet Disord. 2018. PMID: 29348710 Free PMC article.
-
The PTPN22 R263Q polymorphism confers protection against systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis, while PTPN22 R620W confers susceptibility to Graves' disease in a Mexican population.Inflamm Res. 2017 Sep;66(9):775-781. doi: 10.1007/s00011-017-1056-0. Epub 2017 May 12. Inflamm Res. 2017. PMID: 28500376
-
Defective Early B Cell Tolerance Checkpoints in Patients With Systemic Sclerosis Allow the Production of Self Antigen-Specific Clones.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022 Feb;74(2):307-317. doi: 10.1002/art.41927. Epub 2021 Dec 16. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022. PMID: 34279059 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction and pathogenesis in type 1 diabetes.Immunity. 2010 Apr 23;32(4):468-78. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2010.03.018. Immunity. 2010. PMID: 20412757 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Begovich AB, Carlton VE, Honigberg LA, Schrodi SJ, Chokkalingam AP, Alexander HC, Ardlie KG, Huang Q, Smith AM, Spoerke JM, et al. A missense single-nucleotide polymorphism in a gene encoding a protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTPN22) is associated with rheumatoid arthritis. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2004;75:330–337. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Velaga MR, Wilson V, Jennings CE, Owen CJ, Herington S, Donaldson PT, Ball SG, James RA, Quinton R, Perros P, Pearce SH. The codon 620 tryptophan allele of the lymphoid tyrosine phosphatase (LYP) gene is a major determinant of Graves’ disease. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004;89:5862–5865. - PubMed
-
- Smyth D, Cooper JD, Collins JE, Heward JM, Franklyn JA, Howson JM, Vella A, Nutland S, Rance HE, Maier L, et al. Replication of an association between the lymphoid tyrosine phosphatase locus (LYP/PTPN22) with type 1 diabetes, and evidence for its role as a general autoimmunity locus. Diabetes. 2004;53:3020–3023. - PubMed
-
- Bottini N, Musumeci L, Alonso A, Rahmouni S, Nika K, Rostamkhani M, MacMurray J, Meloni GF, Lucarelli P, Pellecchia M, et al. A functional variant of lymphoid tyrosine phosphatase is associated with type I diabetes. Nat. Genet. 2004;36:337–338. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

