Chlamydia trachomatis infection modulates trophoblast cytokine/chemokine production
- PMID: 19265152
- PMCID: PMC2652680
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.0800764
Chlamydia trachomatis infection modulates trophoblast cytokine/chemokine production
Abstract
It is well established that intrauterine infections can pose a threat to pregnancy by gaining access to the placenta and fetus, and clinical studies have strongly linked bacterial infections with preterm labor. Although Chlamydia trachomatis (Ct) can infect the placenta and decidua, little is known about its effects on trophoblast cell immune function. We have demonstrated that Ct infects trophoblast cells to form inclusions and completes the life cycle within these cells by generating infectious elementary bodies. Moreover, infection with Ct leads to differential modulation of the trophoblast cell's production of cytokines and chemokines. Using two human first trimester trophoblast cell lines, Sw.71 and H8, the most striking feature we found was that Ct infection results in a strong induction of IL-1beta secretion and a concomitant reduction in MCP-1 (CCL2) production in both cell lines. In addition, we have found that Ct infection of the trophoblast results in the cleavage and degradation of NF-kappaB p65. These findings suggest that the effect of a Chlamydia infection on trophoblast secretion of chemokines and cytokines involves both activation of innate immune receptors expressed by the trophoblast and virulence factors secreted into the trophoblast by the bacteria. Such altered trophoblast innate immune responses may have a profound impact on the microenvironment of the maternal-fetal interface and this could influence pregnancy outcome.
Figures

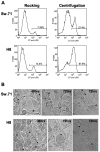
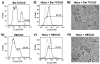
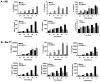


References
-
- Wiesenfeld HC, Hillier SL, Krohn MA, Amortegui AJ, Heine RP, Landers DV, Sweet RL. Lower genital tract infection and endometritis: insight into subclinical pelvic inflammatory disease. Obstet Gynecol. 2002;100:456–463. - PubMed
-
- Hossain A, Arif M, Ramia S, Bakir TF. Chlamydia trachomatis as a cause of abortion. J Hyg Epidemiol Microbiol Immunol. 1990;34:53–55. - PubMed
-
- Jain A, Nag VL, Goel MM, Chandrawati, Chaturvedi UC. Adverse foetal outcome in specific IgM positive Chlamydia trachomatis infection in pregnancy. Indian J Med Res. 1991;94:420–423. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

