Epilysin (MMP-28) restrains early macrophage recruitment in Pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia
- PMID: 19265166
- PMCID: PMC2721855
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.0713949
Epilysin (MMP-28) restrains early macrophage recruitment in Pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia
Abstract
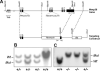
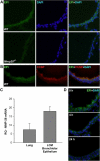
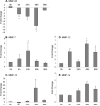
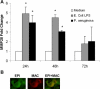
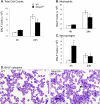
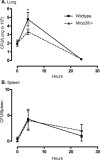
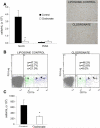
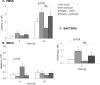
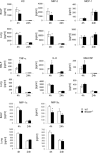
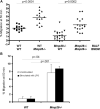
Several members of the matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) family function in various processes of innate immunity, particularly in controlling leukocyte influx. Epilysin (MMP-28) is expressed in numerous tissues and, in adult mice, it has the highest expression in lung, where it is detected in bronchial epithelial cells (Clara cells). Epilysin is also expressed by bone marrow-derived macrophages, but not by alveolar macrophages, suggesting that its expression by macrophages is dependent on localization and differentiation. To assess the role of this MMP, we generated epilysin-null (Mmp28(-/-)) mice. Although epilysin is constitutively expressed in normal tissues, Mmp28(-/-) mice have no overt phenotype. However, using a murine model of Pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia, we found that Mmp28(-/-) mice had an early increase in macrophage recruitment into the lungs, as well as enhanced bacterial clearance and reduced pulmonary neutrophilia, which we predicted were due to accelerated macrophage influx. Macrophage depletion in WT and Mmp28(-/-) mice confirmed a role for macrophages in clearing P. aeruginosa and regulating neutrophil recruitment. Furthermore, we observed that macrophages derived from Mmp28(-/-) mice migrated faster than did wild-type cells to bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from P. aeruginosa-treated mice of either genotype. These observations indicate that epilysin functions as an intrinsic negative regulator of macrophage recruitment by retarding the chemotaxis of these cells.
Figures

References
-
- Suzuki T, Chow CW, Downey GP. Role of innate immune cells and their products in lung immunopathology. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2008;40:1348–1361. - PubMed
-
- Bartlett JA, Fischer AJ, McCray PB., Jr. Innate immune functions of the airway epithelium. Contrib Microbiol. 2008;15:147–163. - PubMed
-
- Kantari C, Pederzoli-Ribeil M, Witko-Sarsat V. The role of neutrophils and monocytes in innate immunity. Contrib Microbiol. 2008;15:118–146. - PubMed
-
- Marriott HM, Dockrell DH. The role of the macrophage in lung disease mediated by bacteria. Exp Lung Res. 2007;33:493–505. - PubMed
-
- Parks WC, Wilson CL, Lopez-Boado YS. Matrix metalloproteinases as modulators of inflammation and innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004;4:617–629. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

