Suppression of lung cancer in murine model: treated by combination of recombinant human endostsatin adenovirus with low-dose cisplatin
- PMID: 19265510
- PMCID: PMC2657125
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-9966-28-31
Suppression of lung cancer in murine model: treated by combination of recombinant human endostsatin adenovirus with low-dose cisplatin
Abstract
Background: The sustained growth of tumors necessitates neovascularization. As one of the potent endogenous vascular inhibitors, endostatin has been widely used in antiangiogenesis therapy for tumor. Cisplatin is normally administered in chemotherapy for lung cancer but accompanied with serious side effects. In the current study, we investigated a novel chemo-antiangiogenesis therapeutic strategy to both improve toxic effects on lung cancer cells and reduce damages to normal cells in the anti-tumor therapy.
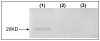
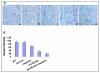
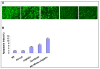
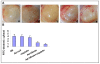
Methods: In vitro, we transduced LLC cells with Ad-hEndo and collected supernatants. Western blotting analysis of the supernatants revealed expression of endostatin. In vivo, to fully investigate the suppression effect on murine lung cancer of the combination therapy, we injected recombinant human endostatin adenovirus intratumorally plus a low dose of cisplatin intraperitoneally routinely. The tumor volume and survival time were observed. Angiogenesis was apparently inhibited within the tumor tissues and on the alginate beads. Assessment of apoptotic cells by the TUNEL assay was conducted in the tumor tissues.
Results: The combination treatment significantly suppressed the tumor growth and prolonged survival time of the murine LLC tumor model. This anti-tumor activity was associated with decreased microvessel density and increased apoptotic index of tumor cells.
Conclusion: According to the results in this study, recombinant human endostatin adenovirus in combination with a low dose of cisplatin demonstrated apparent synergistic anti-tumor activity without marked toxicity. Thus, these observations may provide a rational alternative for lung cancer treatment.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Enhanced efficacy of combination therapy with adeno‑associated virus-delivered pigment epithelium-derived factor and cisplatin in a mouse model of Lewis lung carcinoma.Mol Med Rep. 2014 Jun;9(6):2069-76. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2014.2117. Epub 2014 Apr 4. Mol Med Rep. 2014. PMID: 24714917 Free PMC article.
-
[Suppression of colon cancer in murine model by recombinant human endostatin adenovirus and cisplatin].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2011 Sep;42(5):616-20. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2011. PMID: 22007483 Chinese.
-
Ad-endostatin treatment combined with low-dose irradiation in a murine lung cancer model.Oncol Rep. 2014 Aug;32(2):650-8. doi: 10.3892/or.2014.3253. Epub 2014 Jun 12. Oncol Rep. 2014. PMID: 24927253
-
Gene therapy with the angiogenesis inhibitor endostatin in an orthotopic lung cancer murine model.Hum Gene Ther. 2009 Feb;20(2):103-11. doi: 10.1089/hum.2008.098. Hum Gene Ther. 2009. PMID: 18939902
-
Target therapies in lung cancer.J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011;2011:921231. doi: 10.1155/2011/921231. Epub 2011 Mar 30. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011. PMID: 21541198 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Antimetastatic activity and low systemic toxicity of tetradecyl gallate in a preclinical melanoma mouse model.Invest New Drugs. 2012 Jun;30(3):870-9. doi: 10.1007/s10637-010-9628-7. Epub 2011 Jan 8. Invest New Drugs. 2012. PMID: 21221709
-
Multicenter randomized phase 2 clinical trial of a recombinant human endostatin adenovirus in patients with advanced head and neck carcinoma.Mol Ther. 2014 Jun;22(6):1221-1229. doi: 10.1038/mt.2014.53. Epub 2014 Mar 25. Mol Ther. 2014. PMID: 24662947 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
E10A, an adenovirus-carrying endostatin gene, dramatically increased the tumor drug concentration of metronomic chemotherapy with low-dose cisplatin in a xenograft mouse model for head and neck squamous-cell carcinoma.Cancer Gene Ther. 2012 Feb;19(2):144-52. doi: 10.1038/cgt.2011.79. Epub 2011 Nov 25. Cancer Gene Ther. 2012. PMID: 22116375
-
Molecular genetic analysis of Down syndrome.Hum Genet. 2009 Jul;126(1):195-214. doi: 10.1007/s00439-009-0696-8. Epub 2009 Jun 13. Hum Genet. 2009. PMID: 19526251 Review.
-
Deterministic and Stochastic Study for a Microscopic Angiogenesis Model: Applications to the Lewis Lung Carcinoma.PLoS One. 2016 May 16;11(5):e0155553. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0155553. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27182891 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

