Raltegravir, elvitegravir, and metoogravir: the birth of "me-too" HIV-1 integrase inhibitors
- PMID: 19265512
- PMCID: PMC2660292
- DOI: 10.1186/1742-4690-6-25
Raltegravir, elvitegravir, and metoogravir: the birth of "me-too" HIV-1 integrase inhibitors
Erratum in
- Retrovirology. 2009;6:33
Abstract
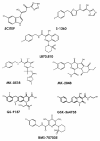
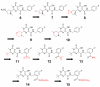
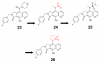
Merck's MK-0518, known as raltegravir, has recently become the first FDA-approved HIV-1 integrase (IN) inhibitor and has since risen to blockbuster drug status. Much research has in turn been conducted over the last few years aimed at recreating but optimizing the compound's interactions with the protein. Resulting me-too drugs have shown favorable pharmacokinetic properties and appear drug-like but, as expected, most have a highly similar interaction with IN to that of raltegravir. We propose that, based upon conclusions drawn from our docking studies illustrated herein, most of these me-too MK-0518 analogues may experience a low success rate against raltegravir-resistant HIV strains. As HIV has a very high mutational competence, the development of drugs with new mechanisms of inhibitory action and/or new active substituents may be a more successful route to take in the development of second- and third-generation IN inhibitors.
Figures

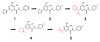


References
-
- UNAIDS AIDS epidemic update. 2007. http://data.unaids.org/pub/EPISlides/2007/2007_epiupdate_en.pdf
-
- The Henry J Kaiser Family Foundation The global HIV/AIDS epidemic. HIV/AIDS Policy Fact Sheet. 2007. http://www.kff.org/hivaids/upload/3030-103.pdf
-
- Klimas N, Koneru AO, Fletcher MA. Overview of HIV. Psychosom Med. 1984;70:523–530. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Using the BED HIV-1 capture EIA assay to estimate incidence using STARHS in the context of surveillance in the United States. 2006. http://data.unaids.org/pub/EPISlides/2006/Statement_BED_Policy_13Dec05_e...
-
- Hammer SM, Eron JJ, Jr, Reiss P, Schooley RT, Thompson MA, Walmsley S, Cahn P, Fischl MA, Gatell JM, Hirsch MS, Jacobsen DM, Montaner JS, Richman DD, Yeni PG, Volberding PA. Antiretroviral treatment of adult HIV infection: 2008 recommendations of the International AIDS Society USA panel. JAMA. 2008;300:555–570. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

