GSK3 beta N-terminus binding to p53 promotes its acetylation
- PMID: 19265551
- PMCID: PMC2660897
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-4598-8-14
GSK3 beta N-terminus binding to p53 promotes its acetylation
Abstract
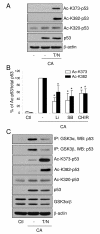
The prevalence in human cancers of mutations in p53 exemplifies its crucial role as a tumor suppressor transcription factor. Previous studies have shown that the constitutively active serine/threonine kinase glycogen synthase kinase-3beta (GSK3 beta) associates with the C-terminal basic domain of p53 and regulates its actions. In this study we identified the GSK3 beta N-terminal amino acids 78-92 as necessary for its association with p53. Inhibitors of GSK3 impaired the acetylation of p53 at Lys373 and Lys382 near the GSK3 beta binding region in p53, indicating that GSK3 beta facilitates p53 acetylation. We also found that acetylation of p53 reduced its association with GSK3 beta, as well as with GSK3alpha. These results indicate that the N-terminal region of GSK3 beta binds p53, this association promotes the acetylation of p53, and subsequently acetylated p53 dissociates from GSK3.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta (GSK3beta) binds to and promotes the actions of p53.J Biol Chem. 2003 Dec 5;278(49):48872-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M305870200. Epub 2003 Sep 30. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 14523002 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear accumulation of glycogen synthase kinase-3 during replicative senescence of human fibroblasts.Aging Cell. 2004 Oct;3(5):309-17. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-9728.2004.00117.x. Aging Cell. 2004. PMID: 15379854 Free PMC article.
-
Glycogen synthase kinase3 beta phosphorylates serine 33 of p53 and activates p53's transcriptional activity.BMC Cell Biol. 2001;2:12. doi: 10.1186/1471-2121-2-12. Epub 2001 Jul 16. BMC Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11483158 Free PMC article.
-
GSK3 in Alzheimer's disease: mind the isoforms.J Alzheimers Dis. 2014;39(4):707-10. doi: 10.3233/JAD-131661. J Alzheimers Dis. 2014. PMID: 24254703 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signaling to p53: breaking the posttranslational modification code.Pathol Biol (Paris). 2000 Apr;48(3):227-45. Pathol Biol (Paris). 2000. PMID: 10858956 Review.
Cited by
-
Compensation between Wnt-driven tumorigenesis and cellular responses to ribosome biogenesis inhibition in the murine intestinal epithelium.Cell Death Differ. 2020 Oct;27(10):2872-2887. doi: 10.1038/s41418-020-0548-6. Epub 2020 Apr 30. Cell Death Differ. 2020. PMID: 32355182 Free PMC article.
-
Coordinating Gene Expression and Axon Assembly to Control Axon Growth: Potential Role of GSK3 Signaling.Front Mol Neurosci. 2012 Feb 6;5:3. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2012.00003. eCollection 2012. Front Mol Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22347166 Free PMC article.
-
GSK3α negatively regulates GSK3β by decreasing its protein levels and enzymatic activity in mouse embryonic stem cells.Stem Cell Reports. 2025 Jul 8;20(7):102512. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2025.102512. Epub 2025 Jun 5. Stem Cell Reports. 2025. PMID: 40480219 Free PMC article.
-
ShenLingLan Influences the Attachment and Migration of Ovarian Cancer Cells Potentially through the GSK3 Pathway.Medicines (Basel). 2017 Feb 21;4(1):10. doi: 10.3390/medicines4010010. Medicines (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28930226 Free PMC article.
-
GSK3α, not GSK3β, drives hippocampal NMDAR-dependent LTD via tau-mediated spine anchoring.EMBO J. 2021 Jan 15;40(2):e105513. doi: 10.15252/embj.2020105513. Epub 2020 Nov 16. EMBO J. 2021. PMID: 33197065 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bax B, Carter PS, Lewis C, Guy AR, Bridges A, Tanner R, Pettman G, Mannix C, Culbert AA, Brown MJB, Smith DG, Reith AD. The structure of phosphorylated GSK-3β complexed with a peptide, FRATtide, that inhibits β-catenin phosphorylation. Structure. 2001;9:1143–1152. doi: 10.1016/S0969-2126(01)00679-7. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

