Anal intercourse among young heterosexuals in three sexually transmitted disease clinics in the United States
- PMID: 19265740
- PMCID: PMC5019823
- DOI: 10.1097/OLQ.0b013e3181901ccf
Anal intercourse among young heterosexuals in three sexually transmitted disease clinics in the United States
Abstract
Objective: To examine factors associated with heterosexual anal intercourse (AI).
Methods: Between 2001 and 2004, 1084 heterosexual adults aged 18 to 26 attending public sexually transmitted disease clinics in Seattle, New Orleans, and St Louis were interviewed using computer-assisted self interview and tested for STIs; Chlamydia trachomatis, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Mycoplasma genitalium, Trichomonas vaginalis, and genital herpes (HSV-2). Characteristics associated with AI were identified using logistic regression.
Results: Overall 400 (37%) reported ever having had AI, 266 (28.9%) reported AI with at least 1 of their last 3 partners, and 19% reported AI with their last partner. Fewer women than men reported condom use at last AI (26% vs. 45%, P <0.001). Ever having AI was associated with sex on the same day as meeting a partner [AOR 3.9 (95% CI, 2.46-6.21)], receiving money for sex [AOR 2.8 (1.40-5.45)], and >3 lifetime sex partners [AOR 2.8 (1.56-5.07)] among women, and sex on the same day as meeting a partner [AOR 2.0 (1.33-3.06]) among men. AI with the last partner was associated with sex toy use [AOR 5.6 (2.63-12.0)] and having concurrent partners [AOR 2.2 (1.21-4.11)] among men, and with sex within a week of meeting [AOR 2.4 (1.28-4.37)], believing the partner was concurrent (AOR 1.9 [1.12-3.22]), and sex toy use [AOR 5.7 (2.31-14.0)] among women. Prevalent vaginal and urethral sexually transmitted infections were not associated with AI.
Conclusions: Many young heterosexuals attending sexually transmitted disease clinics reported AI, which was associated with other sexual risk behaviors, suggesting a confluence of risks for HIV infection.
Figures
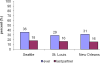


References
-
- Mosher WD, Chandra A, Jones J. Sexual behavior and selected health measures: men and women 15-44 years of age, United States. Adv Data. 2002;2005:1–55. - PubMed
-
- El-Attar SM, Evans DV. Anal warts, sexually transmitted diseases, and anorectal conditions associated with human immunodeficiency virus. Prim Care. 1999;26:81–100. - PubMed
-
- Gross M, Buchbinder SP, Celum C, 3rd., et al. Rectal microbicides for U.S. gay men. Are clinical trials needed? Are they feasible? HIVNET Vaccine Preparedness Study Protocol Team. Sex Transm Dis. 1998;25:296–302. - PubMed
-
- Halperin DT. Heterosexual anal intercourse: prevalence, cultural factors, and HIV infection and other health risks, Part I. AIDS Patient Care STDS. 1999;13:717–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

