Pioglitazone treatment in type 2 diabetes mellitus when combined with portion control diet modifies the metabolic syndrome
- PMID: 19267711
- PMCID: PMC2748337
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1463-1326.2008.00965.x
Pioglitazone treatment in type 2 diabetes mellitus when combined with portion control diet modifies the metabolic syndrome
Abstract
Background: Treatment with thiazolidinediones (TZDs) produces weight gain.
Objective: To test whether a portion control diet could prevent weight gain during treatment with pioglitazone in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Design: This 16-week randomized, open-label, parallel arm study compared three groups: (i) pioglitazone plus the American Diabetes Association diet (Pio + ADA); (ii) pioglitazone plus a portion control weight loss diet (Pio + PC); (iii) metformin plus the American Diabetes Association diet (Met + ADA). All participants received the same advice about calorie reduction, lifestyle change and exercise.
Methods: Fifty-one men and women with T2DM, naive to TZDs, were randomized to a 16-week study. Pioglitazone (Pio) was titrated to a dose of 45 mg/day and metformin (Met) to a dose of 2 g/day. Fasting blood was collected for lipids, insulin and glycosylated haemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) at baseline and 16 weeks.
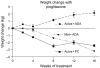
Results: Forty-eight of fifty-one randomized subjects completed the study. Patients treated with Pio + ADA gained 2.15 +/- 1.09 kg (mean +/- SD) compared with a weight loss of 2.59 +/- 1.25 kg (p < 0.05) in the Pio + PC group, and a weight loss of 3.21 +/- 0.7 kg (p < 0.05) in the Met + ADA group. Waist circumference and visceral adipose tissue decreased significantly more in the Pio + PC group than in the Pio + ADA group. High-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels were significantly increased in the Pio + PC group compared with the Met + ADA group. Pioglitazone reduced insulin resistance (homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR)) more than metformin. No significant differences between groups were seen for glucose, insulin, HbA1c or low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels.
Conclusions: Pio + PC, prevented weight gain, reduced waist circumference and visceral fat compared with Pio + ADA diet.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00219440.
Figures
References
-
- Dumasia R, Eagle KA, Kline-Rogers E, et al. Role of PPAR-gamma agonist thiazolidinediones in treatment of pre-diabetic and diabetic individuals: a cardiovascular perspective. Curr Drug Targets Cardiovasc Haematol Disord. 2005;5:377–386. - PubMed
-
- Smith SR, Xie H, Bagnian S, Needham A, McNeil M, Bray GA. Pioglitazone changes the distribution of adipocyte size in type 2 diabetes. Adipocyte. 2006;2:11–22.
-
- Smith SR, De Jonge L, Volaufova J, Li Y, Xie H, Bray GA. Effect of pioglitazone on body composition and energy expenditure: a randomized controlled trial. Metabolism. 2005;54:24–32. - PubMed
-
- Miyazaki Y, Mahankali A, Matsuda M, et al. Effect of pioglitazone on abdominal fat distribution and insulin sensitivity in type 2 diabetic patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002;87:2784–2791. - PubMed
-
- Rasouli N, Raue U, Miles LM, et al. Pioglitazone improves insulin sensitivity through reduction in muscle lipid and redistribution of lipid into adipose tissue. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2005;288:E930–E934. Epub 4 Jan 2005. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous