Reproducibility of RTVue retinal nerve fiber layer thickness and optic disc measurements and agreement with Stratus optical coherence tomography measurements
- PMID: 19268891
- PMCID: PMC3465966
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajo.2008.12.032
Reproducibility of RTVue retinal nerve fiber layer thickness and optic disc measurements and agreement with Stratus optical coherence tomography measurements
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate RTVue spectral-domain optical coherence tomography (OCT) (Optovue Inc, Fremont, California, USA) reproducibility and to assess agreement with Stratus time-domain OCT (Carl Zeiss Meditec, Dublin, California, USA) measurements.
Design: Observational clinical study.
Methods: Scans were obtained from both eyes of all participants 3 times using the RTVue nerve head map 4-mm diameter protocol and once using Stratus OCT within the same session. RTVue reproducibility and agreement with Stratus OCT were evaluated for retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) and optic disc measurements.
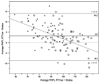
Results: Thirty healthy participants (60 eyes) and 38 glaucoma patients (76 eyes) were included in the study. RTVue reproducibility was good in both healthy participants and patients. For average RNFL thickness, the intraclass correlation coefficients in healthy eyes and patient eyes were 0.97 whereas for rim area they were 0.97 and 0.96, respectively. The correlation between RTVue and Stratus measurements generally was good, especially for average RNFL thickness (healthy eyes and patient eyes, r(2) = 0.82 and 0.86, respectively) and rim volume (healthy eyes and patient eyes, r(2) = 0.78 and 0.76, respectively). Bland-Altman plots showed good agreement between the instruments, with better agreement for average RNFL thickness (95% limits of agreement in healthy eyes and patient eyes, -8.6 to 12 microm and -5.6 to -14.8 microm, respectively) than optic disc parameters. Cup-to-disc ratio 95% limits of agreement in healthy eyes and patient eyes were -0.3 to 0.4 and -0.2 to 0.3, respectively. Optic disc measurements with RTVue were smaller than those with Stratus OCT (eg, disc area was on average 0.4 mm(2) smaller and rim area was 0.3 mm(2) smaller with RTVue).
Conclusions: Reproducibility of RTVue RNFL and optic disc measurements was excellent in both groups. The level of agreement between RTVue and Stratus measurements suggests that RTVue has the potential to detect glaucomatous structural changes.
Figures

References
-
- Blumenthal EZ, Williams JM, Weinreb RN, et al. Reproducibility of nerve fiber layer thickness measurements by use of optical coherence tomography. Ophthalmology. 2000;107:2278–2282. - PubMed
-
- Chen TC, Cense B, Pierce MC, et al. Spectral-domain optical coherence tomography: ultra high-speed, ultra high-resolution ophthalmic imaging. Arch Ophthalmol. 2005;123:1715–1720. - PubMed
-
- Fujimoto JG, Bouma B, Tearney GJ, et al. New technology for high-speed and high-resolution optical coherence tomography. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1998;838:95–107. - PubMed
-
- Leitgeb R, Hitzenberger CK, Fercher AF. Performance of Fourier-domain vs. time-domain optical coherence tomography. Opt Express. 2003;11:889–894. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

