Penta-O-galloyl-beta-D-glucose induces S- and G(1)-cell cycle arrests in prostate cancer cells targeting DNA replication and cyclin D1
- PMID: 19269999
- PMCID: PMC2675654
- DOI: 10.1093/carcin/bgp059
Penta-O-galloyl-beta-D-glucose induces S- and G(1)-cell cycle arrests in prostate cancer cells targeting DNA replication and cyclin D1
Abstract
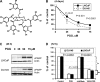
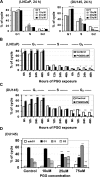
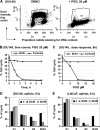
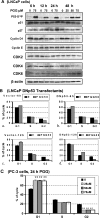
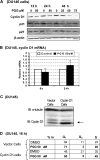
We have recently shown that penta-1,2,3,4,6-O-galloyl-beta-D-glucose (PGG), a naturally occurring hydrolyzable gallotannin, inhibited the in vivo growth of human androgen-independent p53-mutant DU145 prostate cancer (PCa) xenograft in athymic nude mice without adverse effect on their body weight. We have also shown that PGG induced caspase-mediated apoptosis in the DU145 cells and the androgen-dependent human p53-wild-type LNCaP cells. Here, we investigated the cell cycle effects of PGG in these and other PCa cells. Our data show that treatment with subapoptotic doses of PGG induced S-arrest, whereas higher doses of PGG induced not only S-arrest but also G(1) arrest. We show, for the first time, that irrespective of the p53 functional status of the PCa cell lines, PGG exerted a rapid (within 2 h) and potent inhibition (inhibitory concentration by 50% approximately 6 microM) of 5-bromo-2'-deoxyuridine incorporation into S phase cells. In isolated nuclei, PGG inhibited DNA replicative synthesis with superior efficacy than a known DNA polymerase alpha inhibitor, aphidocolin. In addition to the S-arrest action, we have found a close association of downregulation of cyclin D1 with G(1) arrest induced by PGG. Overexpressing this G(1) cyclin abolished G(1) arrest, but hastened the S-arrest induction by PGG. Together, our data indicate that PGG induced PCa S-arrest probably through DNA replicative blockage and induced G(1) arrest via cyclin D1 downregulation to contribute to anticancer activity. Our data raise the hypothesis that PGG may be a novel inhibitor of DNA polymerases.
Figures

References
-
- Lambert JD, et al. Inhibition of carcinogenesis by polyphenols: evidence from laboratory investigations. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005;81:284S–291S. - PubMed
-
- Singh RP, et al. Mechanisms of action of novel agents for prostate cancer chemoprevention. Endocr. Relat. Cancer. 2006;13:751–778. - PubMed
-
- Hu H, et al. Penta-1,2,3,4,6-O-galloyl-beta-D-glucose induces p53 and inhibits STAT3 in prostate cancer cells in vitro and suppresses prostate xenograft tumor growth in vivo. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2008;7:2681–2691. - PubMed
-
- Pan MH, et al. Induction of apoptosis by penta-O-galloyl-beta-D-glucose through activation of caspase-3 in human leukemia HL-60 cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1999;381:171–183. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

