Plasmodium falciparum heterochromatin protein 1 binds to tri-methylated histone 3 lysine 9 and is linked to mutually exclusive expression of var genes
- PMID: 19270070
- PMCID: PMC2677873
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkp115
Plasmodium falciparum heterochromatin protein 1 binds to tri-methylated histone 3 lysine 9 and is linked to mutually exclusive expression of var genes
Abstract
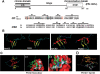
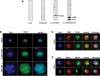
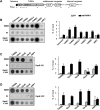
Increasing experimental evidence shows a prominent role of histone modifications in the coordinated control of gene expression in the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. The search for the histone-mark-reading machinery that translates histone modifications into biological processes, such as formation of heterochromatin and antigenic variation is of foremost importance. In this work, we identified the first member of a histone modification specific recognition protein, an orthologue of heterochromatin protein 1 (PfHP1). Analysis of the PfHP1 amino-acid sequence revealed the presence of the two characteristic HP1 domains: a chromodomain (CD) and a chromo shadow domain (CSD). Recombinant CD binds to di- and tri-methylated lysine 9 from histone H3, but not to unmodified or methylated histone H3 in lysine 4. PfHP1 is able to interact with itself to form dimers, underlying its potential role in aggregating nucleosomes to form heterochromatin. Antibodies raised against PfHP1 detect this molecule in foci at the perinuclear region. ChIP analysis using anti-PfHP1 shows that this protein is linked to heterochromatin of subtelomeric non-coding repeat regions and monoallelic expression of the major virulence var gene family. This is the first report implicating an HP1 protein in the control of antigenic variation of a protozoan parasite.
Figures
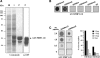


Similar articles
-
Telomeric heterochromatin in Plasmodium falciparum.J Biomed Biotechnol. 2010;2010:290501. doi: 10.1155/2010/290501. Epub 2010 Feb 11. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2010. PMID: 20169127 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Investigation of Heterochromatin Protein 1 Function in the Malaria Parasite Plasmodium falciparum Using a Conditional Domain Deletion and Swapping Approach.mSphere. 2021 Feb 3;6(1):e01220-20. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.01220-20. mSphere. 2021. PMID: 33536327 Free PMC article.
-
Plasmodium falciparum heterochromatin protein 1 marks genomic loci linked to phenotypic variation of exported virulence factors.PLoS Pathog. 2009 Sep;5(9):e1000569. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000569. Epub 2009 Sep 4. PLoS Pathog. 2009. PMID: 19730695 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping and functional analysis of heterochromatin protein 1 phosphorylation in the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum.Sci Rep. 2019 Nov 13;9(1):16720. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-53325-9. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31723180 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical and structural properties of heterochromatin protein 1: understanding its role in chromatin assembly.J Biochem. 2014 Jul;156(1):11-20. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvu032. Epub 2014 May 13. J Biochem. 2014. PMID: 24825911 Review.
Cited by
-
Epigenetic and Epitranscriptomic Gene Regulation in Plasmodium falciparum and How We Can Use It against Malaria.Genes (Basel). 2022 Sep 27;13(10):1734. doi: 10.3390/genes13101734. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36292619 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A view on the role of epigenetics in the biology of malaria parasites.PLoS Pathog. 2012;8(12):e1002943. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002943. Epub 2012 Dec 13. PLoS Pathog. 2012. PMID: 23271963 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Sexual development in Plasmodium parasites: knowing when it's time to commit.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2015 Sep;13(9):573-87. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro3519. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26272409 Review.
-
Telomeric heterochromatin in Plasmodium falciparum.J Biomed Biotechnol. 2010;2010:290501. doi: 10.1155/2010/290501. Epub 2010 Feb 11. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2010. PMID: 20169127 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A var gene upstream element controls protein synthesis at the level of translation initiation in Plasmodium falciparum.PLoS One. 2014 Jun 17;9(6):e100183. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0100183. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24937593 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Le Roch KG, Zhou Y, Blair PL, Grainger M, Moch JK, Haynes JD, De la Vega P, Holder AA, Batalov S, Carucci DJ, et al. Discovery of gene function by expression profiling of the malaria parasite life sycle. Science. 2003;301:1503–1508. - PubMed
-
- Aravind L, Iyer LM, Wellems TE, Miller LH. Plasmodium biology: genomic gleanings. Cell. 2003;115:771–785. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

