Development and application of a novel peptide nucleic acid probe for the specific detection of Cronobacter genomospecies (Enterobacter sakazakii) in powdered infant formula
- PMID: 19270117
- PMCID: PMC2681712
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.02470-08
Development and application of a novel peptide nucleic acid probe for the specific detection of Cronobacter genomospecies (Enterobacter sakazakii) in powdered infant formula
Abstract
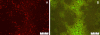
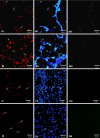
Here, we report a fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) method for rapid detection of Cronobacter strains in powdered infant formula (PIF) using a novel peptide nucleic acid (PNA) probe. Laboratory tests with several Enterobacteriaceae species showed that the specificity and sensitivity of the method were 100%. FISH using PNA could detect as few as 1 CFU per 10 g of Cronobacter in PIF after an 8-h enrichment step, even in a mixed population containing bacterial contaminants.
Figures
References
-
- Amann, R., and B. M. Fuchs. 2008. Single-cell identification in microbial communities by improved fluorescence in situ hybridization techniques. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 6:339-348. - PubMed
-
- Amann, R., F. O. Glockner, and A. Neef. 1997. Modern methods in subsurface microbiology: in situ identification of microorganisms with nucleic acid probes. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 20:191-200.
-
- Becker, H., G. Schaller, W. von Wiese, and G. Terplan. 1994. Bacillus cereus in infant foods and dried milk products. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 23:1-15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

