Bcl-2 antagonists interact synergistically with bortezomib in DLBCL cells in association with JNK activation and induction of ER stress
- PMID: 19270531
- PMCID: PMC2902989
- DOI: 10.4161/cbt.8.9.8131
Bcl-2 antagonists interact synergistically with bortezomib in DLBCL cells in association with JNK activation and induction of ER stress
Erratum in
-
Correction.Cancer Biol Ther. 2019;20(9):1300. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2019.1618578. Epub 2019 May 22. Cancer Biol Ther. 2019. PMID: 31116086 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
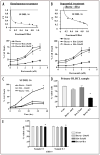
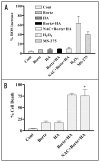
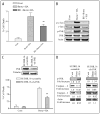
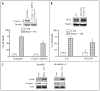
Mechanisms underlying interactions between the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib and small molecule Bcl-2 antagonists were examined in GC- and ABC-type human DLBCL (diffuse lymphocytic B-cell lymphoma) cells. Concomitant or sequential exposure to non- or minimally toxic concentrations of bortezomib or other proteasome inhibitors and either HA14-1 or gossypol resulted in a striking increase in Bax/Bak conformational change/translocation, cytochrome c release, caspase activation and synergistic induction of apoptosis in both GC- and ABC-type cells. These events were associated with a sharp increase in activation of the stress kinase JNK and evidence of ER stress induction (e.g., eIF2alpha phosphorylation, activation of caspases-2 and -4, and Grp78 upregulation). Pharmacologic or genetic (e.g., shRNA knockdown) interruption of JNK signaling attenuated HA14-1/bortezomib lethality and ER stress induction. Genetic disruption of the ER stress pathway (e.g., in cells expressing caspase-4 shRNA or DN-eIF2alpha) significantly attenuated lethality. The toxicity of this regimen was independent of ROS generation. Finally, HA14-1 significantly increased bortezomib-mediated JNK activation, ER stress induction, and lethality in bortezomib-resistant cells. Collectively these findings indicate that small molecule Bcl-2 antagonists promote bortezomib-mediated mitochondrial injury and lethality in DLBCL cells in association with enhanced JNK activation and ER stress induction. They also raise the possibility that such a strategy may be effective in different DLBCL sub-types (e.g., GC- or ABC), and in bortezomib-resistant disease.
Figures


Comment in
-
Piling up the JNK: drug synergy through ER stress.Cancer Biol Ther. 2009 May;8(9):820-2. doi: 10.4161/cbt.8.9.8403. Cancer Biol Ther. 2009. PMID: 19458484 No abstract available.
-
Findings of Research Misconduct.NIH Guide Grants Contracts (Bethesda). 2015 Dec 18:NOT-OD-16-040. NIH Guide Grants Contracts (Bethesda). 2015. PMID: 26693581 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Findings of Research Misconduct.Fed Regist. 2015 Dec 10;80(237):76703-76704. Fed Regist. 2015. PMID: 27737268 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Coiffier B. Non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas. In: Cavalli F, Hansen HH, Kaye SB, editors. Textbook of medical oncology. London: Martin Dunitz; 1997. pp. 34–5.
-
- Coiffier B, Lepage E, Briere J, Herbrecht R, Tilly H, Bouabdallah R, et al. CHOP chemotherapy plus rituximab compared with CHOP alone in elderly patients with diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:235–42. - PubMed
-
- Alizadeh AA, Eisen MB, Davis RE, Ma C, Lossos IS, Rosenwald A, et al. Distinct types of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identified by gene expression profiling. Nature. 2000;403:503–11. - PubMed
-
- Rosenwald A, Wright G, Chan WC, Connors JM, Campo E, Fisher RI, et al. The use of molecular profiling to predict survival after chemotherapy for diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:1937–47. - PubMed
-
- Lossos IS, Jones CD, Warnke R, Natkunam Y, Kaizer H, Zehnder JL, et al. Expression of a single gene, BCL-6, strongly predicts survival in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood. 2001;98:945–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
