Observational study of patient-ventilator asynchrony and relationship to sedation level
- PMID: 19272542
- PMCID: PMC2676917
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2008.08.011
Observational study of patient-ventilator asynchrony and relationship to sedation level
Abstract
Purpose: Clinicians frequently administer sedation to facilitate mechanical ventilation. The purpose of this study was to examine the relationship between sedation level and patient-ventilator asynchrony.
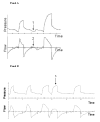
Materials and methods: Airway pressure and airflow were recorded for 15 minutes. Patient-ventilator asynchrony was assessed by determining the number of breaths demonstrating ineffective triggering, double triggering, short cycling, and prolonged cycling. Ineffective triggering index (ITI) was calculated by dividing the number of ineffectively triggered breaths by the total number of breaths (triggered and ineffectively triggered). Sedation level was assessed by the following 3 methods: Richmond Agitation-Sedation Scale (RASS), awake (yes or no), and delirium (Confusion Assessment Method for the intensive care unit [CAM-ICU]).
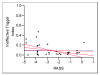
Results: Twenty medical ICU patients underwent 35 observations. Ineffective triggering was seen in 17 of 20 patients and was the most frequent asynchrony (88% of all asynchronous breaths), being observed in 9% +/- 12% of breaths. Deeper levels of sedation were associated with increasing ITI (awake, yes 2% vs no 11%; P < .05; CAM-ICU, coma [15%] vs delirium [5%] vs no delirium [2%]; P < .05; RASS, 0, 0% vs -5, 15%; P < .05). Diagnosis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, sedative type or dose, mechanical ventilation mode, and trigger method had no effect on ITI.
Conclusions: Asynchrony is common, and deeper sedation level is a predictor of ineffective triggering.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Thille AW, Rodriguez P, Cabello B, et al. Patient-ventilator asynchrony during mechanical ventilation: Prevalence and risk factors. Intensive Care Med. 2006;32:1515–1522. - PubMed
-
- Fabry B, Guttmann J, Eberhard L, et al. An analysis of desynchronization between the spontaneously breathing patient and ventilator during inspiratory pressure support. Chest. 1995;107:1387–1394. - PubMed
-
- Nava S, Bruschi C, Fracchia C, et al. Patient-ventilator interaction and inspiratory effort during pressure support ventilation in patients with different pathologies. Eur Respir J. 1997;10:177–183. - PubMed
-
- Purro A, Appendini L, De Gaetano A, et al. Physiologic determinants of ventilator dependence in long-term mechanically ventilated patients. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000;161:1115–1123. - PubMed
-
- Chao DC, Scheinhorn DJ, Stearn-Hassenpflug M. Patient-ventilator trigger asynchrony in prolonged mechanical ventilation. Chest. 1997;112:1592–1599. - PubMed

