Is the drip-and-ship approach to delivering thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke safe?
- PMID: 19272734
- PMCID: PMC2891901
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jemermed.2008.10.018
Is the drip-and-ship approach to delivering thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke safe?
Abstract
Background: The drip-and-ship method of treating stroke patients may increase the use of tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA) in community hospitals.
Objective: The safety and early outcomes of patients treated with t-PA for acute ischemic stroke (AIS) by the drip-and-ship method were compared to patients directly treated at a stroke center.
Methods: The charts of all patients who were treated with intravenous (i.v.) t-PA at outside hospitals under the remote guidance of our stroke team and were then transferred to our facility were reviewed. Baseline NIHSS (National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale) scores, onset-to-treatment (OTT), and arrival-to-treatment (ATT) times were abstracted. The rates of in-hospital mortality, symptomatic hemorrhage (sICH), early excellent outcome (modified Rankin Scale [mRS] ≤ 1), and early good outcome (discharge home or to inpatient rehabilitation) were determined.
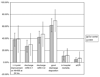
Results: One hundred sixteen patients met inclusion criteria. Eighty-four (72.4%) were treated within 3 h of symptom onset. The median estimated NIHSS score was 9.5 (range 3-27). The median OTT time was 150 min, and the median ATT was 85 min. These patients had an in-hospital mortality rate of 10.7% and sICH rate of 6%. Thirty percent of patients had an early excellent outcome and 75% were discharged to home or inpatient rehabilitation. When these outcome rates were compared with those observed in patients treated directly at our stroke center, there were no statistical differences.
Conclusions: In this small retrospective study, drip-and-ship management of delivering i.v. t-PA for AIS patients did not seem to compromise safety. However, a large prospective study comparing drip-and-ship management to routine care is needed to validate the safety of this approach to treatment.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Katzan IL, Furlan AJ, Lloyd LE, et al. Use of tissue-type plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke: the Cleveland area experience. JAMA. 2000;283:1151–1158. - PubMed
-
- Reed SD, Cramer SC, Blough DK, Meyer K, Jarvik JG. Treatment with tissue plasminogen activator and inpatient mortality rates for patients with ischemic stroke treated in community hospitals. Stroke. 2001;32:1832–1840. - PubMed
-
- Chan YF, Kwiatkowski TG, Rella JG, et al. Tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke: a New York city emergency medicine perspective. J Emerg Med. 2005;29:405–408. - PubMed
-
- Kothari RU, Brott T, Broderick JP, Hamilton CA. Emergency physicians. Accuracy in the diagnosis of stroke. Stroke. 1995;26:2238–2241. - PubMed
-
- Morgenstern LB, Lisabeth LD, Mecozzi AC, et al. A population-based study of acute stroke and TIA diagnosis. Neurology. 2004;62:895–900. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

