Diversity of polyproline recognition by EVH1 domains
- PMID: 19273103
- PMCID: PMC3882067
- DOI: 10.2741/3281
Diversity of polyproline recognition by EVH1 domains
Abstract
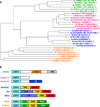
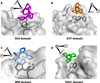
Enabled/VASP Homology-1 (EVH1) domains function primarily as interaction modules that link signaling proteins by binding to proline-rich sequences. EVH1 domains are ~115 residues in length and adopt the pleckstrin homology (PH) fold. Four different protein families contain EVH1 domains: Ena/VASP, Homer, WASP and SPRED. Except for the SPRED domains, for which no binding partners are known, EVH1 domains use a conserved hydrophobic cleft to bind a four-residue motif containing 2-4 prolines. Conserved aromatic residues, including an invariant tryptophan, create a wedge-shaped groove on the EVH1 surface that matches the triangular profile of a polyproline type II helix. Hydrophobic residues adjacent to the polyproline motif dock into complementary sites on the EVH1 domain to enhance ligand binding specificity. Pseudosymmetry in the polyproline type II helix allows peptide ligands to bind in either of two N-to-C terminal orientations, depending on interactions between sequences flanking the prolines and the EVH1 domain. EVH1 domains also recognize non-proline motifs, as illustrated by the structure of an EVH1:LIM3 complex and the extended EVH1 ligands of the verprolin family.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Aromatic and basic residues within the EVH1 domain of VASP specify its interaction with proline-rich ligands.Curr Biol. 1999 Jul 1;9(13):715-8. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(99)80315-7. Curr Biol. 1999. PMID: 10498433
-
Dual epitope recognition by the VASP EVH1 domain modulates polyproline ligand specificity and binding affinity.EMBO J. 2000 Sep 15;19(18):4903-14. doi: 10.1093/emboj/19.18.4903. EMBO J. 2000. PMID: 10990454 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the Interaction Landscape of the EVH1 Domain of Mena.Biochemistry. 2024 Sep 3;63(17):2183-2195. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.4c00331. Epub 2024 Aug 13. Biochemistry. 2024. PMID: 39138154 Free PMC article.
-
Doing (F/L)PPPPs: EVH1 domains and their proline-rich partners in cell polarity and migration.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2002 Feb;14(1):88-103. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(01)00299-x. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11792550 Review.
-
EVH1 domains: structure, function and interactions.FEBS Lett. 2002 Feb 20;513(1):45-52. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(01)03291-4. FEBS Lett. 2002. PMID: 11911879 Review.
Cited by
-
Chromosome Translocation t(10;19)(q26;q13) in a CIC-sarcoma.In Vivo. 2023 Jan-Feb;37(1):57-69. doi: 10.21873/invivo.13054. In Vivo. 2023. PMID: 36593014 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiovascular Functions of Ena/VASP Proteins: Past, Present and Beyond.Cells. 2023 Jun 28;12(13):1740. doi: 10.3390/cells12131740. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37443774 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A requirement for filopodia extension toward Slit during Robo-mediated axon repulsion.J Cell Biol. 2016 Apr 25;213(2):261-74. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201509062. Epub 2016 Apr 18. J Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27091449 Free PMC article.
-
TANGO1/cTAGE5 receptor as a polyvalent template for assembly of large COPII coats.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Sep 6;113(36):10061-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1605916113. Epub 2016 Aug 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27551091 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Insights into the SPRED1-Neurofibromin-KRAS Complex and Disruption of SPRED1-Neurofibromin Interaction by Oncogenic EGFR.Cell Rep. 2020 Jul 21;32(3):107909. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.107909. Cell Rep. 2020. PMID: 32697994 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pawson T, Nash P. Assembly of cell regulatory systems through protein interaction domains. Science. 2003;300:445–452. - PubMed
-
- Copley RR, Doerks T, Letunic I, Bork P. Protein domain analysis in the era of complete genomes. FEBS Lett. 2002;513:129–134. - PubMed
-
- Harris BZ, Lim WA. Mechanism and role of PDZ domains in signaling complex assembly. J Cell Sci. 2001;114:3219–3231. - PubMed
-
- Pawson T, Gish GD, Nash P. SH2 domains, interaction modules and cellular wiring. Trends Cell Biol. 2001;11:504–511. - PubMed
-
- Zarrinpar A, Bhattacharyya RP, Lim WA. The structure and function of proline recognition domains. Sci STKE. 2003;2003:RE8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

