Key players in chromosome segregation in Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 19273145
- PMCID: PMC2745088
- DOI: 10.2741/3323
Key players in chromosome segregation in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
In contrast to many eukaryotic organisms in which kinetochores are assembled on localized centromeres of monocentric chromosomes, Caenorhabditis elegans has diffuse kinetochores, termed holo-kinetochores, which are assembled along the entire length of the mitotic chromosome. Despite this cytologically distinct chromosomal architecture, holo-kinetochores of C. elegans and kinetochores of other eukaryotes share structurally and functionally conserved properties. The amphitelic attachment of sister kinetochores to microtubules can be achieved by proper chromosomal organization, which relies on spatiotemporally orchestrated functions of conserved protein complexes such as the cohesin, condensin, and chromosomal passenger complexes during mitosis and meiosis in C. elegans. Moreover, the structure of spindle assembly checkpoint components and their safeguard function are also well conserved in C. elegans. Extensive efforts in the last few years to elucidate the molecular mechanisms of the C. elegans spindle assembly checkpoint have revealed its unique features. In this review, I will focus on the conservation and diversity of proteins that are required to maintain chromosome transmission fidelity during mitosis and meiosis in C. elegans.
Figures


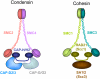


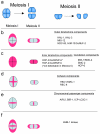
Similar articles
-
"Holo"er than thou: chromosome segregation and kinetochore function in C. elegans.Chromosome Res. 2004;12(6):641-53. doi: 10.1023/B:CHRO.0000036588.42225.2f. Chromosome Res. 2004. PMID: 15289669 Review.
-
The aurora B kinase AIR-2 regulates kinetochores during mitosis and is required for separation of homologous Chromosomes during meiosis.Curr Biol. 2002 May 14;12(10):798-812. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(02)00820-5. Curr Biol. 2002. PMID: 12015116
-
Synergistic stabilization of microtubules by BUB-1, HCP-1, and CLS-2 controls microtubule pausing and meiotic spindle assembly.Elife. 2023 Feb 17;12:e82579. doi: 10.7554/eLife.82579. Elife. 2023. PMID: 36799894 Free PMC article.
-
C. elegans condensin promotes mitotic chromosome architecture, centromere organization, and sister chromatid segregation during mitosis and meiosis.Genes Dev. 2002 Mar 15;16(6):729-42. doi: 10.1101/gad.968302. Genes Dev. 2002. PMID: 11914278 Free PMC article.
-
Role of chromosomes in assembly of meiotic and mitotic spindles.Prog Cell Cycle Res. 1997;3:271-84. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-5371-7_22. Prog Cell Cycle Res. 1997. PMID: 9552422 Review.
Cited by
-
Spermatogenesis.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013;757:171-203. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-4015-4_7. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013. PMID: 22872478 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression of human Bcl-xL (Ser49) and (Ser62) mutants in Caenorhabditis elegans causes germline defects and aneuploidy.PLoS One. 2017 May 8;12(5):e0177413. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0177413. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28481930 Free PMC article.
-
The spindle assembly checkpoint in Caenorhabditis elegans: one who lacks Mad1 becomes mad one.Cell Cycle. 2009 Feb 1;8(3):338-44. doi: 10.4161/cc.8.3.7448. Epub 2009 Feb 17. Cell Cycle. 2009. PMID: 19177000 Free PMC article.
-
Mitotic Cell Division in Caenorhabditis elegans.Genetics. 2019 Jan;211(1):35-73. doi: 10.1534/genetics.118.301367. Genetics. 2019. PMID: 30626640 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alternative meiotic chromatid segregation in the holocentric plant Luzula elegans.Nat Commun. 2014 Oct 8;5:4979. doi: 10.1038/ncomms5979. Nat Commun. 2014. PMID: 25296379 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

