Mechanism of cytokine modulation of epithelial tight junction barrier
- PMID: 19273235
- PMCID: PMC3724223
- DOI: 10.2741/3413
Mechanism of cytokine modulation of epithelial tight junction barrier
Abstract
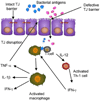
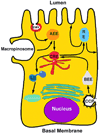
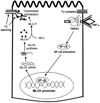
Cytokines play a crucial role in the modulation of inflammatory response in the gastrointestinal tract. Pro-inflammatory cytokines including tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interferon-gamma, interleukin-1beta?IL-1beta?, and interleukin-12 are essential in mediating the inflammatory response, while anti-inflammatory cytokines including interleukin-10 and transforming growth factor-beta are important in the attenuation or containment of inflammatory process. It is increasingly recognized that cytokines have an important physiological and pathological effect on intestinal tight junction (TJ) barrier. Consistent with their known pro-inflammatory activities, pro-inflammatory cytokines cause a disturbance in intestinal TJ barrier, allowing increased tissue penetration of luminal antigens. Recent studies indicate that the inhibition of cytokine induced increase in intestinal TJ permeability has an important protective effect against intestinal mucosal damage and development of intestinal inflammation. In this review, the effects of various pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines on intestinal TJ barrier and the progress into the mechanisms that mediate the cytokine modulation of intestinal TJ barrier are reviewed.
Figures

References
-
- Ma T, Madara J. Tight Junctions and the intestinal barrier. In: Johnson R, editor. Textbook of Gastrointestinal Physiology. Burlington, Ma: Elsevier Academic Press; 2006.
-
- Nusrat A, Turner JR, Madara JL. Molecular physiology and pathophysiology of tight junctions. IV. Regulation of tight junctions by extracellular stimuli: nutrients, cytokines, and immune cells. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2000;279:G851–G857. - PubMed
-
- DeMeo M, Mutlu EA, Keshavarzian A, Tobin MC. Intestinal permeation and gastrointestinal disease. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2002;34:385–396. - PubMed
-
- Bruewer M, Samarin S, Nusrat A. Inflammatory bowel disease and the apical junctional complex. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006;1072:242–252. - PubMed
-
- Shen L, Turner JR. Role of epithelial cells in initiation and propagation of intestinal inflammation. Eliminating the static: tight junction dynamics exposed. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2006;290:G577–G582. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

