DNA damage induced p53 downregulates Cdc20 by direct binding to its promoter causing chromatin remodeling
- PMID: 19273532
- PMCID: PMC2677870
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkp110
DNA damage induced p53 downregulates Cdc20 by direct binding to its promoter causing chromatin remodeling
Abstract
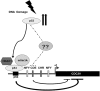
CDC20 is a critical molecule in the Spindle Assembly Checkpoint (SAC). It activates the Anaphase promoting complex and helps a dividing cell to proceed towards Anaphase. CDC20 is overexpressed in many tumor cells which cause chromosomal instability. There have been limited reports on the mechanism of SAC's response to genotoxic stress. We show that ectopically expressed p53 or DNA damage induced endogenous p53 can downregulate Cdc20 transcriptionally. We have identified a consensus p53-binding site on the Cdc20 promoter and have shown that it is being used by p53 to bind the promoter and bring about chromatin remodeling thereby repressing Cdc20. Additionally, p53 also downregulates Cdc20 promoter through CDE/CHR element, but in a p21 independent manner. This CDE/CHR element-mediated downregulation occurs only under p53 overexpressed condition but not in the context of DNA damage. The present results suggest that the two CCAAT elements in the Cdc20 promoter are not used by p53 to downregulate its activity, as reported earlier.
Figures


References
-
- Musacchio A, Salmon ED. The spindle-assembly checkpoint in space and time. Nature Rev. 2007;8:379–393. - PubMed
-
- Sihn CR, Suh EJ, Lee KH, Kim TY, Kim SH. p55CDC/hCDC20 mutant induces mitotic catastrophe by inhibiting the MAD2-dependent spindle checkpoint activity in tumor cells. Cancer Lett. 2003;201:203–210. - PubMed
-
- Yoon YM, Baek KH, Jeong SJ, Shin HJ, Ha GH, Jeon AH, Hwang SG, Chun JS, Lee CW. WD repeat-containing mitotic checkpoint proteins act as transcriptional repressors during interphase. FEBS Lett. 2004;575:23–29. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

