Intramolecular disulfide bonds of the prolactin receptor short form are required for its inhibitory action on the function of the long form of the receptor
- PMID: 19273600
- PMCID: PMC2682051
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01716-08
Intramolecular disulfide bonds of the prolactin receptor short form are required for its inhibitory action on the function of the long form of the receptor
Abstract
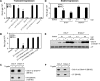
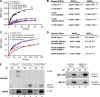
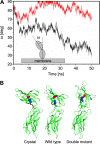
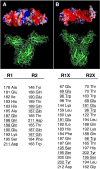
The short form (S1b) of the prolactin receptor (PRLR) silences prolactin-induced activation of gene transcription by the PRLR long form (LF). The functional and structural contributions of two intramolecular disulfide (S-S) bonds within the extracellular subdomain 1 (D1) of S1b to its inhibitory function on the LF were investigated. Mutagenesis of the paired cysteines eliminated the inhibitory action of S1b. The expression of the mutated S1b (S1bx) on the cell surface was not affected, indicating native-like folding of the receptor. The constitutive JAK2 phosphorylation observed in S1b was not present in cells expressing S1bx, and JAK2 association was disrupted. BRET(50) (BRET(50) represents the relative affinity as acceptor/donor ratio required to reach half-maximal BRET [bioluminescence resonance energy transfer] values) showed decreased LF/S1bx heterodimeric-association and increased affinity in S1bx homodimerization, thus favoring LF homodimerization and prolactin-induced signaling. Computer modeling based on the PRLR crystal structure showed that minor changes in the tertiary structure of D1 upon S-S bond disruption propagated to the quaternary structure of the homodimer, affecting the dimerization interface. These changes explain the higher homodimerization affinity of S1bx and provide a structural basis for its lack of inhibitory function. The PRLR conformation as stabilized by S-S bonds is required for the inhibitory action of S1b on prolactin-induced LF-mediated function and JAK2 association.
Figures

References
-
- Acosta, J. J., R. M. Munoz, L. Gonzalez, A. Subtil-Rodriguez, M. A. Dominguez-Caceres, J. M. Garcia-Martinez, A. Calcabrini, I. Lazaro-Trueba, and J. Martin-Perez. 2003. Src mediates prolactin-dependent proliferation of T47D and MCF7 cells via the activation of focal adhesion kinase/Erk1/2 and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathways. Mol. Endocrinol. 172268-2282. - PubMed
-
- Ali, S., and S. Ali. 2000. Recruitment of the protein-tyrosine phosphatase SHP-2 to the C-terminal tyrosine of the prolactin receptor and to the adaptor protein Gab2. J. Biol. Chem. 27539073-39080. - PubMed
-
- Aman, M. J., T. S. Migone, A. Sasaki, D. P. Ascherman, M. Zhu, E. Soldaini, K. Imada, A. Miyajima, A. Yoshimura, and W. J. Leonard. 1999. CIS associates with the interleukin-2 receptor beta chain and inhibits interleukin-2-dependent signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 27430266-30272. - PubMed
-
- Bazan, J. F. 1989. A novel family of growth factor receptors: a common binding domain in the growth hormone, prolactin, erythropoietin and IL-6 receptors, and the p75 IL-2 receptor beta-chain. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 164788-795. - PubMed
-
- Bole-Feysot, C., V. Goffin, M. Edery, N. Binart, and P. A. Kelly. 1998. Prolactin (PRL) and its receptor: actions, signal transduction pathways and phenotypes observed in PRL receptor knockout mice. Endocr. Rev. 19225-268. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
