Thymus-homing peripheral dendritic cells constitute two of the three major subsets of dendritic cells in the steady-state thymus
- PMID: 19273629
- PMCID: PMC2699131
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20082232
Thymus-homing peripheral dendritic cells constitute two of the three major subsets of dendritic cells in the steady-state thymus
Abstract
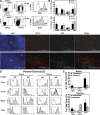
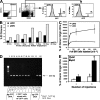
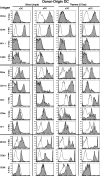
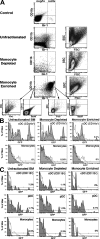
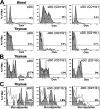
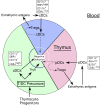
Many dendritic cells (DCs) in the normal mouse thymus are generated intrathymically from common T cell/DC progenitors. However, our previous work suggested that at least 50% of thymic DCs originate independently of these progenitors. We now formally demonstrate by parabiotic, adoptive transfer, and developmental studies that two of the three major subsets of thymic DCs originate extrathymically and continually migrate to the thymus, where they occupy a finite number of microenvironmental niches. The thymus-homing DCs consisted of immature plasmacytoid DCs (pDCs) and the signal regulatory protein alpha-positive (Sirpalpha(+)) CD11b(+) CD8alpha(-) subset of conventional DCs (cDCs), both of which could take up and transport circulating antigen to the thymus. The cDCs of intrathymic origin were mostly Sirpalpha(-) CD11b(-) CD8alpha(hi) cells. Upon arrival in the thymus, the migrant pDCs enlarged and up-regulated CD11c, major histocompatibility complex II (MHC II), and CD8alpha, but maintained their plasmacytoid morphology. In contrast, the migrant cDCs proliferated extensively, up-regulated CD11c, MHC II, and CD86, and expressed dendritic processes. The possible functional implications of these findings are discussed.
Figures

References
-
- Wu L., Shortman K. 2005. Heterogeneity of thymic dendritic cells.Semin. Immunol. 17:304–312 - PubMed
-
- Donskoy E., Goldschneider I. 2003. Two developmentally distinct populations of dendritic cells inhabit the adult mouse thymus: demonstration by differential importation of hematogenous precursors under steady state conditions.J. Immunol. 170:3514–3521 - PubMed
-
- Wang Y., Goldschneider I., Foss D., Wu D.Y., O'Rourke J., Cone R.E. 1997. Direct thymic involvement in anterior chamber-associated immune deviation: evidence for a nondeletional mechanism of centrally induced tolerance to extrathymic antigens in adult mice.J. Immunol. 158:2150–2155 - PubMed
-
- Wang Y., Goldschneider I., O'Rourke J., Cone R.E. 2001. Blood mononuclear cells induce regulatory NK T thymocytes in anterior chamber-associated immune deviation.J. Leukoc. Biol. 69:741–746 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

