Concurrent titration and determination of antibiotic resistance in ureaplasma species with identification of novel point mutations in genes associated with resistance
- PMID: 19273669
- PMCID: PMC2681543
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01349-08
Concurrent titration and determination of antibiotic resistance in ureaplasma species with identification of novel point mutations in genes associated with resistance
Abstract
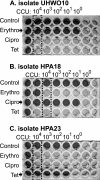
Antibiotic resistance determination of Ureaplasma spp. (Ureaplasma parvum and Ureaplasma urealyticum) usually requires predetermination of bacterial titer, followed by antibiotic interrogation using a set bacterial input. This 96-well method allows simultaneous quantification of bacteria in the presence and absence of antibiotics. A method for determining precise MICs and a method for screening against multiple antibiotics using breakpoint thresholds are detailed. Of the 61 Ureaplasma-positive clinical isolates screened, one (1.6%) was resistant to erythromycin (MIC, >64 mg/liter) and clarithromycin (MIC, 4 mg/liter), one to ciprofloxacin (1.6%), and one to tetracycline/doxycycline (1.6%). Five isolates were also consistently found to have an elevated MIC of 8 mg/liter for erythromycin, but this may not represent true antibiotic resistance, as no mutations were found in the 23S rRNA operons or ribosome-associated L4 and L22 proteins for these strains. However, two amino acids (R66Q67) were deleted from the L4 protein of the erythromycin-/clarithromycin-resistant strain. The tetM genetic element was detected in the tetracycline-resistant clinical isolate as well as in the positive control Vancouver strain serotype 9. The tetM gene was also found in a fully tetracycline-susceptible Ureaplasma clinical isolate, and no mutations were found in the coding region that would explain its failure to mediate tetracycline resistance. An amino acid substitution (D82N) was found in the ParC subunit of the ciprofloxacin-resistant isolate, adjacent to the S83L mutation reported by other investigators in many ciprofloxacin-resistant Ureaplasma isolates. It is now possible to detect antibiotic resistance in Ureaplasma within 48 h of positive culture without prior knowledge of bacterial load, identifying them for further molecular analysis.
Figures
References
-
- Abele-Horn, M., J. Peters, O. Genzel-Boroviczeny, C. Wolff, A. Zimmermann, and W. Gottschling. 1997. Vaginal Ureaplasma urealyticum colonization: influence on pregnancy outcome and neonatal morbidity. Infection 25:286-291. - PubMed
-
- Bebear, C. M., H. Renaudin, A. Charron, D. Gruson, M. Lefrancois, and C. Bebear. 2000. In vitro activity of trovafloxacin compared to those of five antimicrobials against mycoplasmas including Mycoplasma hominis and Ureaplasma urealyticum fluoroquinolone-resistant isolates that have been genetically characterized. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 44:2557-2560. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Blanchard, A., D. M. Crabb, K. Dybvig, L. B. Duffy, and G. H. Cassell. 1992. Rapid detection of tetM in Mycoplasma hominis and Ureaplasma urealyticum by PCR: tetM confers resistance to tetracycline but not necessarily to doxycycline. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 74:277-281. - PubMed
-
- Blanchard, A., J. Hentschel, L. Duffy, K. Baldus, and G. H. Cassell. 1993. Detection of Ureaplasma urealyticum by polymerase chain reaction in the urogenital tract of adults, in amniotic fluid, and in the respiratory tract of newborns. Clin. Infect. Dis. 17(Suppl. 1):S148-S153. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

