G-protein-coupled receptor kinase interacting protein-1 is required for pulmonary vascular development
- PMID: 19273721
- PMCID: PMC2732662
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.823997
G-protein-coupled receptor kinase interacting protein-1 is required for pulmonary vascular development
Abstract
Background: The G-protein-coupled receptor kinase interacting protein-1 (GIT1) is a multidomain scaffold protein that participates in many cellular functions including receptor internalization, focal adhesion remodeling, and signaling by both G-protein-coupled receptors and tyrosine kinase receptors. However, there have been no in vivo studies of GIT1 function to date.
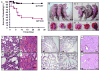
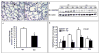
Methods and results: To determine essential functions of GIT1 in vivo, we generated a traditional GIT1 knockout mouse. GIT1 knockout mice exhibited approximately 60% perinatal mortality. Pathological examination showed that the major abnormality in GIT1 knockout mice was impaired lung development characterized by markedly reduced numbers of pulmonary blood vessels and increased alveolar spaces. Given that vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is essential for pulmonary vascular development, we investigated the role of GIT1 in VEGF signaling in the lung and cultured endothelial cells. Because activation of phospholipase-Cgamma (PLCgamma) and extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1/2 (ERK1/2) by angiotensin II requires GIT1, we hypothesized that GIT1 mediates VEGF-dependent pulmonary angiogenesis by modulating PLCgamma and ERK1/2 activity in endothelial cells. In cultured endothelial cells, knockdown of GIT1 decreased VEGF-mediated phosphorylation of PLCgamma and ERK1/2. PLCgamma and ERK1/2 activity in lungs from GIT1 knockout mice was reduced postnatally.
Conclusions: Our data support a critical role for GIT1 in pulmonary vascular development by regulating VEGF-induced PLCgamma and ERK1/2 activation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



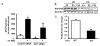

Similar articles
-
G-protein-coupled receptor-2-interacting protein-1 is required for endothelial cell directional migration and tumor angiogenesis via cortactin-dependent lamellipodia formation.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014 Feb;34(2):419-26. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.113.302689. Epub 2013 Nov 21. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014. PMID: 24265417 Free PMC article.
-
GIT1 mediates VEGF-induced podosome formation in endothelial cells: critical role for PLCgamma.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2009 Feb;29(2):202-8. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.108.174391. Epub 2008 Nov 20. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2009. PMID: 19023093 Free PMC article.
-
GIT1Y321 phosphorylation is required for ERK1/2- and PDGF-dependent VEGF secretion from osteoblasts to promote angiogenesis and bone healing.Int J Mol Med. 2012 Oct;30(4):819-25. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2012.1058. Epub 2012 Jul 12. Int J Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 22797318
-
GPCR kinase 2 interacting protein 1 (GIT1) regulates osteoclast function and bone mass.J Cell Physiol. 2010 Nov;225(3):777-85. doi: 10.1002/jcp.22282. J Cell Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20568227 Free PMC article.
-
The multifunctional GIT family of proteins.J Cell Sci. 2006 Apr 15;119(Pt 8):1469-75. doi: 10.1242/jcs.02925. J Cell Sci. 2006. PMID: 16598076 Review.
Cited by
-
Phosphorylation of GIT1 tyrosine 321 is required for association with FAK at focal adhesions and for PDGF-activated migration of osteoblasts.Mol Cell Biochem. 2012 Jun;365(1-2):109-18. doi: 10.1007/s11010-012-1249-3. Mol Cell Biochem. 2012. PMID: 22302306
-
Early epigenetic changes of Alzheimer's disease in the human hippocampus.Epigenetics. 2020 Oct;15(10):1083-1092. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2020.1748917. Epub 2020 Apr 7. Epigenetics. 2020. PMID: 32233750 Free PMC article.
-
Neonatal hyperoxia causes pulmonary vascular disease and shortens life span in aging mice.Am J Pathol. 2011 Jun;178(6):2601-10. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.02.010. Epub 2011 May 6. Am J Pathol. 2011. PMID: 21550015 Free PMC article.
-
Microcephaly with altered cortical layering in GIT1 deficiency revealed by quantitative neuroimaging.Magn Reson Imaging. 2021 Feb;76:26-38. doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2020.09.023. Epub 2020 Sep 30. Magn Reson Imaging. 2021. PMID: 33010377 Free PMC article.
-
Proximity based proteomics reveals Git1 as a regulator of Smoothened signaling.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jan 7:2025.01.06.631593. doi: 10.1101/2025.01.06.631593. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 39829937 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
-
- Premont RT, Claing A, Vitale N, Freeman JL, Pitcher JA, Patton WA, Moss J, Vaughan M, Lefkowitz RJ. beta2-Adrenergic receptor regulation by GIT1, a G protein-coupled receptor kinase-associated ADP ribosylation factor GTPase-activating protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998;95:14082–7. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Premont RT, Claing A, Vitale N, Perry SJ, Lefkowitz RJ. The GIT family of ADP-ribosylation factor GTPase-activating proteins. Functional diversity of GIT2 through alternative splicing. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:22373–80. - PubMed
-
- Schmalzigaug R, Phee H, Davidson CE, Weiss A, Premont RT. Differential Expression of the ARF GAP Genes GIT1 and GIT2 in Mouse Tissues. J Histochem Cytochem. 2007 - PubMed
-
- Hoefen RJ, Berk BC. The multifunctional GIT family of proteins. J Cell Sci. 2006;119:1469–75. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

