Anaplastic lymphoma kinase: role in cancer pathogenesis and small-molecule inhibitor development for therapy
- PMID: 19275511
- PMCID: PMC2780428
- DOI: 10.1586/14737140.9.3.331
Anaplastic lymphoma kinase: role in cancer pathogenesis and small-molecule inhibitor development for therapy
Abstract
Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK), a receptor tyrosine kinase in the insulin receptor superfamily, was initially identified in constitutively activated oncogenic fusion forms - the most common being nucleophosmin-ALK - in anaplastic large-cell lymphomas, and subsequent studies have identified ALK fusions in diffuse large B-cell lymphomas, systemic histiocytosis, inflammatory myofibroblastic tumors, esophageal squamous cell carcinomas and non-small-cell lung carcinomas. More recently, genomic DNA amplification and protein overexpression, as well as activating point mutations, of ALK have been described in neuroblastomas. In addition to those cancers for which a causative role for aberrant ALK activity is well validated, more circumstantial links implicate the full-length, normal ALK receptor in the genesis of other malignancies - including glioblastoma and breast cancer - via a mechanism of receptor activation involving autocrine and/or paracrine growth loops with the reported ALK ligands, pleiotrophin and midkine. This review summarizes normal ALK biology, the confirmed and putative roles of ALK in the development of human cancers and efforts to target ALK using small-molecule kinase inhibitors.
Figures


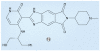
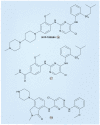
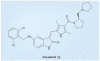

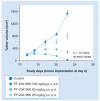
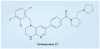
References
-
- Schlessinger J. Cell signalling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell. 2000;103:211–225. - PubMed
-
- Kolibaba KS, Druker BJ. Protein kinases and cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1997;1333:F217–F248. - PubMed
-
- Blume-Jensen P, Hunter T. Oncogenic kinase signalling. Nature. 2001;411:355–365. - PubMed
-
- Scheijen B, Griffin JD. Tyrosine kinase oncogenes in normal hematopoiesis and hematological disease. Oncogene. 2002;21:3314–3333. - PubMed
-
-
Morris SW, Kirstein MN, Valentine MB, et al. Fusion of a kinase gene, ALK, to a nucleolar protein gene, NPM, in non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Science. 1994;263:1281–1284.Describes the initial cloning and characterization of nucleolar protein nucleophosmin (NPM)–anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK).
-
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
