GlcNAcstatins are nanomolar inhibitors of human O-GlcNAcase inducing cellular hyper-O-GlcNAcylation
- PMID: 19275764
- PMCID: PMC2691177
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20090110
GlcNAcstatins are nanomolar inhibitors of human O-GlcNAcase inducing cellular hyper-O-GlcNAcylation
Abstract
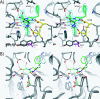
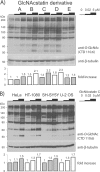
O-GlcNAcylation is an essential, dynamic and inducible post-translational glycosylation of cytosolic proteins in metazoa and can show interplay with protein phosphorylation. Inhibition of OGA (O-GlcNAcase), the enzyme that removes O-GlcNAc from O-GlcNAcylated proteins, is a useful strategy to probe the role of this modification in a range of cellular processes. In the present study, we report the rational design and evaluation of GlcNAcstatins, a family of potent, competitive and selective inhibitors of human OGA. Kinetic experiments with recombinant human OGA reveal that the GlcNAcstatins are the most potent human OGA inhibitors reported to date, inhibiting the enzyme in the sub-nanomolar to nanomolar range. Modification of the GlcNAcstatin N-acetyl group leads to up to 160-fold selectivity against the human lysosomal hexosaminidases which employ a similar substrate-assisted catalytic mechanism. Mutagenesis studies in a bacterial OGA, guided by the structure of a GlcNAcstatin complex, provides insight into the role of conserved residues in the human OGA active site. GlcNAcstatins are cell-permeant and, at low nanomolar concentrations, effectively modulate intracellular O-GlcNAc levels through inhibition of OGA, in a range of human cell lines. Thus these compounds are potent selective tools to study the cell biology of O-GlcNAc.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cell-penetrant, nanomolar O-GlcNAcase inhibitors selective against lysosomal hexosaminidases.Chem Biol. 2010 Nov 24;17(11):1250-5. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2010.09.014. Chem Biol. 2010. PMID: 21095575 Free PMC article.
-
Screening-based discovery of drug-like O-GlcNAcase inhibitor scaffolds.FEBS Lett. 2010 Feb 19;584(4):694-700. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2009.12.020. Epub 2009 Dec 16. FEBS Lett. 2010. PMID: 20026047 Free PMC article.
-
Elevation of cellular O-GlcNAcylation level by a potent and selective O-GlcNAcase inhibitor based on tetrahydroimidazopyridine scaffold.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2012 Nov 15;22(22):6854-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2012.09.042. Epub 2012 Sep 23. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2012. PMID: 23058883
-
O-GlcNAcase: Emerging Mechanism, Substrate Recognition and Small-Molecule Inhibitors.ChemMedChem. 2020 Jul 20;15(14):1244-1257. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.202000077. Epub 2020 Jun 16. ChemMedChem. 2020. PMID: 32496638 Review.
-
O-GlcNAcase: promiscuous hexosaminidase or key regulator of O-GlcNAc signaling?J Biol Chem. 2014 Dec 12;289(50):34433-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R114.609198. Epub 2014 Oct 21. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25336650 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dissecting PUGNAc-mediated inhibition of the pro-survival action of insulin.Glycobiology. 2016 Nov;26(11):1198-1208. doi: 10.1093/glycob/cww043. Epub 2016 Apr 12. Glycobiology. 2016. PMID: 27072814 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical arsenal for the study of O-GlcNAc.Molecules. 2011 Feb 28;16(3):1987-2022. doi: 10.3390/molecules16031987. Molecules. 2011. PMID: 21358590 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Monitoring protein O-linked β-N-acetylglucosamine status via metabolic labeling and copper-free click chemistry.Anal Biochem. 2014 Nov 1;464:70-2. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2014.06.010. Epub 2014 Jul 1. Anal Biochem. 2014. PMID: 24995865 Free PMC article.
-
An efficient and versatile synthesis of GlcNAcstatins-potent and selective O-GlcNAcase inhibitors built on the tetrahydroimidazo[1,2-a]pyridine scaffold.Tetrahedron. 2010 Sep 25;66(39-3):7838-7849. doi: 10.1016/j.tet.2010.07.037. Tetrahedron. 2010. PMID: 20976183 Free PMC article.
-
Role of O-Linked N-Acetylglucosamine Protein Modification in Cellular (Patho)Physiology.Physiol Rev. 2021 Apr 1;101(2):427-493. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00043.2019. Epub 2020 Jul 30. Physiol Rev. 2021. PMID: 32730113 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Torres C. R, Hart G. W. Topography and polypeptide distribution of terminal N-acetylglucosamine residues on the surfaces of intact lymphocytes: evidence for O-linked GlcNAc. J. Biol. Chem. 1984;259:3308–3317. - PubMed
-
- Zachara N. E., Hart G. W. O-GlcNAc modification: a nutritional sensor that modulates proteasome function. Trends Cell Biol. 2004;14:218–221. - PubMed
-
- Love D. C., Hanover J. A. The hexosamine signaling pathway: deciphering the “O-GlcNAc code”. Science STKE. 2005;312:1–14. - PubMed
-
- Hart G. W., Housley M. P., Slawson C. Cycling of O-linked β-N-acetylglucosamine on nucleocytoplasmic proteins. Nature. 2007;446:1017–1022. - PubMed
-
- Chou T. Y., Hart G. W. O-linked N-acetylglucosamine and cancer: messages from the glycosylation of c-Myc. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2001;491:413–418. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

