Dendritic assembly of heteromeric gamma-aminobutyric acid type B receptor subunits in hippocampal neurons
- PMID: 19276079
- PMCID: PMC2676040
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M900575200
Dendritic assembly of heteromeric gamma-aminobutyric acid type B receptor subunits in hippocampal neurons
Abstract
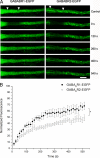
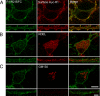
Understanding the mechanisms that control synaptic efficacy through the availability of neurotransmitter receptors depends on uncovering their specific intracellular trafficking routes. gamma-Aminobutyric acid type B (GABA(B)) receptors (GABA(B)Rs) are obligatory heteromers present at dendritic excitatory and inhibitory postsynaptic sites. It is unknown whether synthesis and assembly of GABA(B)Rs occur in the somatic endoplasmic reticulum (ER) followed by vesicular transport to dendrites or whether somatic synthesis is followed by independent transport of the subunits for assembly and ER export throughout the somatodendritic compartment. To discriminate between these possibilities we studied the association of GABA(B)R subunits in dendrites of hippocampal neurons combining live fluorescence microscopy, biochemistry, quantitative colocalization, and bimolecular fluorescent complementation. We demonstrate that GABA(B)R subunits are segregated and differentially mobile in dendritic intracellular compartments and that a high proportion of non-associated intracellular subunits exist in the brain. Assembled heteromers are preferentially located at the plasma membrane, but blockade of ER exit results in their intracellular accumulation in the cell body and dendrites. We propose that GABA(B)R subunits assemble in the ER and are exported from the ER throughout the neuron prior to insertion at the plasma membrane. Our results are consistent with a bulk flow of segregated subunits through the ER and rule out a post-Golgi vesicular transport of preassembled GABA(B)Rs.
Figures




References
-
- Collingridge, G. L., Isaac, J. T., and Wang, Y. T. (2004) Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 5 952-962 - PubMed
-
- Inoue, A., and Okabe, S. (2003) Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 13 332-340 - PubMed
-
- Moss, S. J., and Smart, T. G. (2001) Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2 240-250 - PubMed
-
- Clem, R. L., and Barth, A. (2006) Neuron 49 663-670 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

