Tolerance induction in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis using non-myeloablative hematopoietic gene therapy with autoantigen
- PMID: 19277013
- PMCID: PMC2835141
- DOI: 10.1038/mt.2009.42
Tolerance induction in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis using non-myeloablative hematopoietic gene therapy with autoantigen
Erratum in
- Mol Ther. 2009 Jul;17(7):1303
-
Corrigendum to "Tolerance Induction in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis Using Non-myeloablative Hematopoietic Gene Therapy With Autoantigen".Mol Ther. 2009 Jul;17(7):1303. doi: 10.1038/mt.2009.69. Epub 2016 Dec 6. Mol Ther. 2009. PMID: 28178479 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
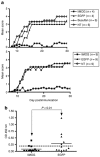
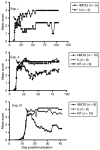
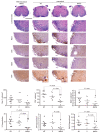
Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) constitutes a paradigm of antigen (Ag)-specific T cell driven autoimmune diseases. In this study, we transferred bone marrow cells (BMCs) expressing an autoantigen (autoAg), the peptide 40-55 of the myelin oligodendrocytic glycoprotein (MOG(40-55)), to induce preventive and therapeutic immune tolerance in a murine EAE model. Transfer of BMC expressing MOG(40-55) (IiMOG-BMC) into partially myeloablated mice resulted in molecular chimerism and in robust protection from the experimental disease. In addition, in mice with established EAE, transfer of transduced BMC with or without partial myeloablation reduced the clinical and histopathological severity of the disease. In these experiments, improvement was observed even in the absence of engraftment of the transduced hematopoietic cells, probably rejected due to the previous immunization with the autoAg. Splenocytes from mice transplanted with IiMOG-BMC produced significantly higher amounts of interleukin (IL)-5 and IL-10 upon autoAg challenge than those of control animals, suggesting the participation of regulatory cells. Altogether, these results suggest that different tolerogenic mechanisms may be mediating the preventive and the therapeutic effects. In conclusion, this study demonstrates that a cell therapy using BMC expressing an autoAg can induce Ag-specific tolerance and ameliorate established EAE even in a nonmyeloablative setting.
Figures




References
-
- Bracy JL, Sachs DH., and , Iacomini J. Inhibition of xenoreactive natural antibody production by retroviral gene therapy. Science. 1998;281:1845–1847. - PubMed
-
- Wekerle T., and , Sykes M. Mixed chimerism and transplantation tolerance. Annu Rev Med. 2001;52:353–370. - PubMed
-
- Emery DW, Sablinski T, Shimada H, Germana S, Gianello P, Foley A, et al. Expression of an allogeneic MHC DRB transgene, through retroviral transduction of bone marrow, induces specific reduction of alloreactivity. Transplantation. 1997;64:1414–1423. - PubMed
-
- Bagley J, Tian C, Sachs DH., and , Iacomini J. Induction of T-cell tolerance to an MHC class I alloantigen by gene therapy. Blood. 2002;99:4394–4399. - PubMed
-
- Alderuccio F, Murphy K., and , Toh BH. Stem cells engineered to express self antigen to treat autoimmunity. Trends Immunol. 2003;24:176–180. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

