The emerging role of nuclear architecture in DNA repair and genome maintenance
- PMID: 19277046
- PMCID: PMC3478884
- DOI: 10.1038/nrm2651
The emerging role of nuclear architecture in DNA repair and genome maintenance
Abstract
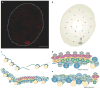
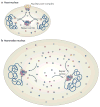
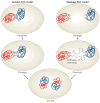
DNA repair and maintenance of genome stability are crucial to cellular and organismal function, and defects in these processes have been implicated in cancer and ageing. Detailed molecular, biochemical and genetic analyses have outlined the molecular framework involved in cellular DNA-repair pathways, but recent cell-biological approaches have revealed important roles for the spatial and temporal organization of the DNA-repair machinery during the recognition of DNA lesions and the assembly of repair complexes. It has also become clear that local higher-order chromatin structure, chromatin dynamics and non-random global genome organization are key factors in genome maintenance. These cell-biological features of DNA repair illustrate an emerging role for nuclear architecture in multiple aspects of genome maintenance.
Figures


References
-
- Wyman C, Kanaar R. DNA double-strand break repair: all’s well that ends well. Annu Rev Genet. 2006;40:363–383. - PubMed
-
- Lobrich M, Jeggo PA. The impact of a negligent G2/M checkpoint on genomic instability and cancer induction. Nature Rev Cancer. 2007;7:861–869. - PubMed
-
- Lukas J, Lukas C, Bartek J. Mammalian cell cycle checkpoints: signalling pathways and their organization in space and time. DNA Repair. 2004;3:997–1007. - PubMed
-
- Misteli T. Beyond the sequence: cellular organization of genome function. Cell. 2007;128:787–800. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

