Roles of protein-disulfide isomerase-mediated disulfide bond formation of yeast Mnl1p in endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation
- PMID: 19279007
- PMCID: PMC2673250
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M900813200
Roles of protein-disulfide isomerase-mediated disulfide bond formation of yeast Mnl1p in endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation
Abstract
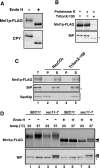
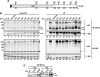
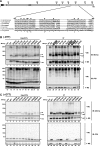
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) has a strict protein quality control system. Misfolded proteins generated in the ER are degraded by the ER-associated degradation (ERAD). Yeast Mnl1p consists of an N-terminal mannosidase homology domain and a less conserved C-terminal domain and facilitates the ERAD of glycoproteins. We found that Mnl1p is an ER luminal protein with a cleavable signal sequence and stably interacts with a protein-disulfide isomerase (PDI). Analyses of a series of Mnl1p mutants revealed that interactions between the C-terminal domain of Mnl1p and PDI, which include an intermolecular disulfide bond, are essential for subsequent introduction of a disulfide bond into the mannosidase homology domain of Mnl1p by PDI. This disulfide bond is essential for the ERAD activity of Mnl1p and in turn stabilizes the prolonged association of PDI with Mnl1p. Close interdependence between Mnl1p and PDI suggests that these two proteins form a functional unit in the ERAD pathway.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation (ERAD) and free oligosaccharide generation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.J Biol Chem. 2011 Dec 2;286(48):41786-41800. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.251371. Epub 2011 Oct 6. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21979948 Free PMC article.
-
The contributions of protein disulfide isomerase and its homologues to oxidative protein folding in the yeast endoplasmic reticulum.J Biol Chem. 2004 Nov 26;279(48):49780-6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M409210200. Epub 2004 Sep 17. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15377672
-
Mnl1p, an alpha -mannosidase-like protein in yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, is required for endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation of glycoproteins.J Biol Chem. 2001 Mar 23;276(12):8635-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C100023200. Epub 2001 Jan 31. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11254655
-
Mechanisms of productive folding and endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation of glycoproteins and non-glycoproteins.Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2021 Mar;1865(3):129812. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2020.129812. Epub 2020 Dec 11. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2021. PMID: 33316349 Review.
-
Oxidoreductases in Glycoprotein Glycosylation, Folding, and ERAD.Cells. 2020 Sep 22;9(9):2138. doi: 10.3390/cells9092138. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32971745 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Htm1p-Pdi1p is a folding-sensitive mannosidase that marks N-glycoproteins for ER-associated protein degradation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Jul 12;113(28):E4015-24. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1608795113. Epub 2016 Jun 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27357682 Free PMC article.
-
No country for old misfolded glycoproteins.Mol Cell. 2011 Jun 24;42(6):715-7. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2011.06.004. Mol Cell. 2011. PMID: 21700217 Free PMC article.
-
Protein disulfide isomerase 1 is required for RodA assembling-based conidial hydrophobicity of Aspergillus fumigatus.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2024 Apr 17;90(4):e0126023. doi: 10.1128/aem.01260-23. Epub 2024 Mar 19. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38501925 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of early EDEM1 protein maturation events and their functional implications.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jul 15;286(28):24906-15. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.243998. Epub 2011 Jun 1. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21632540 Free PMC article.
-
ER-resident protein 46 (ERp46) triggers the mannose-trimming activity of ER degradation-enhancing α-mannosidase-like protein 3 (EDEM3).J Biol Chem. 2018 Jul 6;293(27):10663-10674. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.003129. Epub 2018 May 21. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29784879 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

