Human T-cell leukemia virus type 2 Rex carboxy terminus is an inhibitory/stability domain that regulates Rex functional activity and viral replication
- PMID: 19279097
- PMCID: PMC2682101
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02271-08
Human T-cell leukemia virus type 2 Rex carboxy terminus is an inhibitory/stability domain that regulates Rex functional activity and viral replication
Abstract
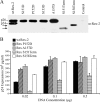
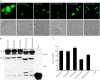
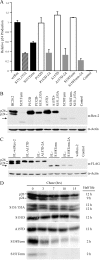
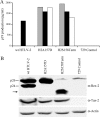
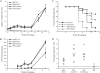
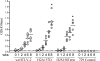
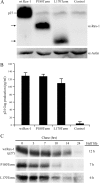
Human T-cell leukemia virus (HTLV) regulatory protein, Rex, functions to increase the expression of the viral structural and enzymatic gene products. The phosphorylation of two serine residues (S151 and S153) at the C terminus is important for the function of HTLV-2 Rex (Rex-2). The Rex-2 phosphomimetic double mutant (S151D, S153D) is locked in a functionally active conformation. Since rex and tax genes overlap, Rex S151D and S153D mutants were found to alter the Tax oncoprotein coding sequence and transactivation activities. Therefore, additional Rex-2 mutants including P152D, A157D, S151Term, and S158Term were generated and characterized ("Term" indicates termination codon). All Rex-2 mutants and wild-type (wt) Rex-2 localized predominantly to the nucleus/nucleolus, but in contrast to the detection of phosphorylated and unphosphorylated forms of wt Rex-2 (p26 and p24), mutant proteins were detected as a single phosphoprotein species. We found that Rex P152D, A157D, and S158Term mutants are more functionally active than wt Rex-2 and that the Rex-2 C terminus and its specific phosphorylation state are required for stability and optimal expression. In the context of the provirus, the more active Rex mutants (A157D or S158Term) promoted increased viral protein production, increased viral infectious spread, and enhanced HTLV-2-mediated cellular proliferation. Moreover, these Rex mutant viruses replicated and persisted in inoculated rabbits despite higher antiviral antibody responses. Thus, we identified in Rex-2 a novel C-terminal inhibitory domain that regulates functional activity and is positively regulated through phosphorylation. The ability of this domain to modulate viral replication likely plays a key role in the infectious spread of the virus and in virus-induced cellular proliferation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Functional domain structure of human T-cell leukemia virus type 2 rex.J Virol. 2003 Dec;77(23):12829-40. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.23.12829-12840.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 14610204 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of two serine residues regulates human T-cell leukemia virus type 2 Rex function.J Virol. 2001 Sep;75(18):8440-8. doi: 10.1128/jvi.75.18.8440-8448.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11507189 Free PMC article.
-
Human T-cell leukemia virus type 2 post-transcriptional control protein p28 is required for viral infectivity and persistence in vivo.Retrovirology. 2008 May 12;5:38. doi: 10.1186/1742-4690-5-38. Retrovirology. 2008. PMID: 18474092 Free PMC article.
-
Tuning Rex rules HTLV-1 pathogenesis.Front Immunol. 2022 Sep 16;13:959962. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.959962. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36189216 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of human T cell leukemia virus expression.FASEB J. 1990 Feb 1;4(2):169-75. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.4.2.2404818. FASEB J. 1990. PMID: 2404818 Review.
Cited by
-
Elucidation of the Mechanism of Host NMD Suppression by HTLV-1 Rex: Dissection of Rex to Identify the NMD Inhibitory Domain.Viruses. 2022 Feb 9;14(2):344. doi: 10.3390/v14020344. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35215946 Free PMC article.
-
Human T-lymphotropic virus proteins and post-translational modification pathways.World J Virol. 2012 Aug 12;1(4):115-30. doi: 10.5501/wjv.v1.i4.115. World J Virol. 2012. PMID: 24175216 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HTLV-1 Rex Tunes the Cellular Environment Favorable for Viral Replication.Viruses. 2016 Feb 24;8(3):58. doi: 10.3390/v8030058. Viruses. 2016. PMID: 26927155 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HTLV-1 Rex: the courier of viral messages making use of the host vehicle.Front Microbiol. 2012 Sep 6;3:330. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2012.00330. eCollection 2012. Front Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22973269 Free PMC article.
-
Post-transcriptional Regulation of HTLV Gene Expression: Rex to the Rescue.Front Microbiol. 2019 Aug 22;10:1958. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.01958. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31507567 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adachi, Y., T. D. Copeland, C. Takahashi, T. Nosaka, A. Ahmed, S. Oroszlan, and M. Hatanaka. 1992. Phosphorylation of the Rex protein of human T-cell leukemia virus type I. J. Biol. Chem. 26721977-21981. - PubMed
-
- Adachi, Y., T. Nosaka, and M. Hatanaka. 1990. Protein kinase inhibitor H-7 blocks accumulation of unspliced mRNA of human T-cell leukemia virus type I (HTLV-II). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 169469-475. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

