MR imaging identification of oligodendroglial hyperplasia
- PMID: 19279283
- PMCID: PMC7051576
- DOI: 10.3174/ajnr.A1522
MR imaging identification of oligodendroglial hyperplasia
Abstract
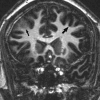
We report a case of oligodendroglial hyperplasia detected by using high-resolution high-field MR imaging. This disorder is considered part of the spectrum of cortical migrational abnormalities and is found with increased incidence in patients with epilepsy. Surgery offers the best chance for cure in patients with medically refractory partial complex epilepsy. Accurate localization and detection of the full lesion extent by using a high-resolution imaging technique such as 3T MR imaging is important to surgical success. Detection of subtle dysplastic lesions such as oligodendroglial hyperplasia may be clinically relevant.
Figures

References
-
- Burger PC, Scheithauer BW, Vogel FS. The brain: surgery for seizures. In: Surgical Pathology of the Nervous System and Its Coverings. 4th ed. New York: Churchill Livingstone;2002
-
- Phal PM, Usmanov A, Nesbit GM, et al. Qualitative comparison of 3-T and 1.5-T MRI in the evaluation of epilepsy. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2008;191:890–95 - PubMed
-
- Cascino GD. Improving quality of life with epilepsy surgery: the seizure outcome is the key to success. Neurology 2007;68:1967–68 - PubMed
-
- Langfitt JT, Holloway RG, McDermott MP, et al. Health care costs decline after successful epilepsy surgery. Neurology 2007;68:1290–98 - PubMed
-
- Wyllie E, Lachhwani DK, Gupta A, et al. Successful surgery for epilepsy due to early brain lesions despite generalized EEG findings. Neurology 2007;69:389–97 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
