Estimation of the serial interval of influenza
- PMID: 19279492
- PMCID: PMC3057478
- DOI: 10.1097/EDE.0b013e31819d1092
Estimation of the serial interval of influenza
Abstract
Background: : Estimates of the clinical-onset serial interval of human influenza infection (time between onset of symptoms in an index case and a secondary case) are used to inform public health policy and to construct mathematical models of influenza transmission. We estimate the serial interval of laboratory-confirmed influenza transmission in households.
Methods: : Index cases were recruited after reporting to a primary healthcare center with symptoms. Members of their households were followed-up with repeated home visits.
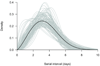
Results: : Assuming a Weibull model and accounting for selection bias inherent in our field study design, we used symptom-onset times from 14 pairs of infector/infectee to estimate a mean serial interval of 3.6 days (95% confidence interval = 2.9-4.3 days), with standard deviation 1.6 days.
Conclusion: : The household serial interval of influenza may be longer than previously estimated. Studies of the complete serial interval, based on transmission in all community contexts, are a priority.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

