Stronger inflammatory/cytotoxic T-cell response in women identified by microarray analysis
- PMID: 19279650
- PMCID: PMC2735332
- DOI: 10.1038/gene.2009.12
Stronger inflammatory/cytotoxic T-cell response in women identified by microarray analysis
Abstract
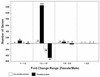
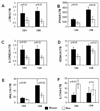
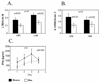
Women develop chronic inflammatory autoimmune diseases more often than men. The mechanisms causing the increased susceptibility are incompletely understood. Chronic immune stimulation characterizes many autoimmune disorders. We hypothesized that repeated stimulation may cause a different T-cell response in women than in men. Microarrays were used to compare gene expression in T cells from healthy men and women with and without repeated stimulation. Four days after a single stimulation, only 25% of differentially expressed, gender-biased genes were expressed at higher levels in women. In contrast, after restimulation, 72% were more highly expressed in women. Immune response genes were significantly over-represented among the genes upregulated in women and among the immune response genes, the inflammatory/cytotoxic effector genes interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma), lymphotoxin beta (LTbeta), granzyme A (GZMA), interleukin-12 receptor beta2 (IL12Rbeta2), and granulysin (GNLY) were among those overexpressed to the highest degree. In contrast, IL17A was the only effector gene more highly expressed in men. Estrogen response elements were identified in the promoters of half the overexpressed immune genes in women, and in <10% of the male-biased genes. The differential expression of inflammatory/cytotoxic effector molecules in restimulated female T cells may contribute to the differences in autoimmune diseases between women and men.
Figures
References
-
- Li J, McMurray RW. Effects of estrogen receptor subtype-selective agonists on autoimmune disease in lupus-prone NZB/NZW F1 mouse model. Clin Immunol. 2007;123(2):219–226. - PubMed
-
- Huang JL, Yao TC, See LC. Prevalence of pediatric systemic lupus erythematosus and juvenile chronic arthritis in a Chinese population: a nation-wide prospective population-based study in Taiwan. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2004;22(6):776–780. - PubMed
-
- Uekert SJ, Akan G, Evans MD, Li Z, Roberg K, Tisler C, et al. Sex-related differences in immune development and the expression of atopy in early childhood. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006;118(6):1375–1381. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

