Maternal visfatin concentration in normal pregnancy
- PMID: 19284295
- PMCID: PMC3500641
- DOI: 10.1515/JPM.2009.054
Maternal visfatin concentration in normal pregnancy
Abstract
Objective: Adipose tissue has now emerged as a powerful endocrine organ via the production of adipokines. Visfatin, a novel adipokine with diabetogenic and immuno-modulatory properties has been implicated in the pathophysiology of insulin resistance in patients with obesity and Type-2 diabetes mellitus. The aim of this study was to determine whether there are changes in the maternal plasma concentration of visfatin with advancing gestation and as a function of maternal weight.
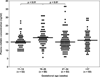
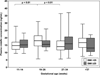
Study design: In this cross-sectional study, maternal plasma concentrations of visfatin were determined in normal weight and overweight/obese pregnant women in the following gestational age groups: 1) 11-14 weeks (n=52); 2) 19-26 weeks (n=68); 3) 27-34 weeks (n=93); and 4) >37 weeks (n=60). Visfatin concentrations were determined by ELISA. Non parametric statistics were used for analysis.
Results: 1) The median maternal plasma visfatin concentration was higher in pregnant women between 19-26 weeks of gestation than that of those between 11-14 weeks of gestation (P<0.01) and those between 27-34 weeks of gestation (P<0.01); 2) among normal weight pregnant women, the median plasma visfatin concentrations of women between 19-26 weeks of gestation was higher than that of those between 11-14 weeks (P<0.01) and those between 27-34 weeks (P<0.01); and 3) among overweight/obese patients, the median maternal visfatin concentration was similar between the different gestational age groups.
Conclusion: The median maternal plasma concentration of visfatin peaks between 19-26 and has a nadir between 27-34 weeks of gestation. Normal and overweight/obese pregnant women differed in the pattern of changes in circulating visfatin concentrations as a function of gestational age.
Figures
References
-
- Diet, nutrition and the prevention of chronic diseases. World Health Organ Tech.Rep.Ser. 2003;916 i-149, backcover. - PubMed
-
- Supplement 1. American Diabetes Association: clinical practice recommendations 2000. Diabetes Care. 2000;23(Suppl 1):S1–S116. - PubMed
-
- Abrams B, Carmichael S, Selvin S. Factors associated with the pattern of maternal weight gain during pregnancy. Obstet.Gynecol. 1995;86:170–176. - PubMed
-
- Acromite M, Ziotopoulou M, Orlova C, Mantzoros C. Increased leptin levels in preeclampsia: associations with BMI estrogen and SHBG levels. Hormones.(Athens.) 2004;3:46–52. - PubMed
-
- Alessi MC, Peiretti F, Morange P, Henry M, Nalbone G, Juhan-Vague I. Production of plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 by human adipose tissue: possible link between visceral fat accumulation and vascular disease. Diabetes. 1997;46:860–867. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
