Dynamics of the expression of intermediate filaments vimentin and desmin during myofibroblast differentiation after corneal injury
- PMID: 19285070
- PMCID: PMC2716066
- DOI: 10.1016/j.exer.2009.02.022
Dynamics of the expression of intermediate filaments vimentin and desmin during myofibroblast differentiation after corneal injury
Abstract
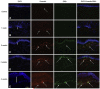
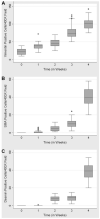
Previous studies have suggested that abnormal corneal wound healing in patients after photorefractive keratectomy (PRK) is associated with the appearance of myofibroblasts in the stroma between two and four weeks after surgery. The purpose of this study was to examine potential myofibroblast progenitor cells that might express other filament markers prior to completion of the differentiation pathway that yields alpha-smooth muscle actin (SMA)-expressing myofibroblasts associated with haze localized beneath the epithelial basement membrane after PRK. Twenty-four female rabbits that had -9 diopter PRK were sacrificed at 1 week, 2 weeks, 3 weeks or 4 weeks after surgery. Corneal rims were collected, frozen at -80 degrees C, and analyzed by immunocytochemistry using anti-vimentin, anti-desmin, and anti-SMA antibodies. Double immunostaining was performed for the co-localization of SMA with vimentin or desmin with SMA. An increase in vimentin expression in stromal cells is noted as early as 1 week after PRK in the rabbit cornea. As the healing response continues at two or three weeks after surgery, many stromal cells expressing vimentin also begin to express desmin and SMA. By 4 weeks after the surgery most, if not all, myofibroblasts express vimentin, desmin and SMA. Generalized least squares regression analysis showed that there was strong evidence that each of the marker groups differed in expression over time compared to the other two (p<0.01). Intermediate filaments--vimentin and desmin co-exist in myofibroblasts along with SMA and may play an important role in corneal remodeling after photorefractive keratectomy. The earliest precursors of myofibroblasts destined to express SMA and desmin are detectible by staining for vimentin at 1 week after surgery.
Figures

References
-
- Ambrosio R, Wilson SE. LASIK vs LASEK vs PRK. Advantages and indications. Semin. Ophthalmol. 2003;18:2–10. - PubMed
-
- Bhawan J, Majno G. The myofibroblast. Possible derivation from macrophages in xanthogranuloma. Am. J. Dermatopathol. 1989;11:255–258. - PubMed
-
- Cooper D, Schermer A, Sun TT. Classification of human epithelia and their neoplasms using monoclonal antibodies to keratins: strategies, applications, and limitations. Lab. Invest. 1985;52:243–256. - PubMed
-
- Direkze NC, Forbes SJ, Brittan M, Hunt T, Jeffery R, Preston SL, Poulsom R, Hodivala-Dilke K, Alison MR, Wright NA. Multiple organ engraftment by bone-marrow-derived myofibroblasts and fibroblasts in bone-marrow-transplanted mice. Stem Cells. 2003;21:514–520. - PubMed
-
- Fini ME. Keratocyte and fibroblast phenotypes in the repairing cornea. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 1999;18:529–551. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

