Lesion mapping of cognitive abilities linked to intelligence
- PMID: 19285465
- PMCID: PMC2728583
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2009.01.026
Lesion mapping of cognitive abilities linked to intelligence
Abstract
The Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS) assesses a wide range of cognitive abilities and impairments. Factor analyses have documented four underlying indices that jointly comprise intelligence as assessed with the WAIS: verbal comprehension (VCI), perceptual organization (POI), working memory (WMI), and processing speed (PSI). We used nonparametric voxel-based lesion-symptom mapping in 241 patients with focal brain damage to investigate their neural underpinnings. Statistically significant lesion-deficit relationships were found in left inferior frontal cortex for VCI, in left frontal and parietal cortex for WMI, and in right parietal cortex for POI. There was no reliable single localization for PSI. Statistical power maps and cross-validation analyses quantified specificity and sensitivity of the index scores in predicting lesion locations. Our findings provide comprehensive lesion maps of intelligence factors, and make specific recommendations for interpretation and application of the WAIS to the study of intelligence in health and disease.
Figures

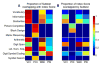
References
-
- Abdi H. In: RV coefficient and congruence coefficient. In Encyclopedia of Measurement and Statistics. Salkind N, editor. Thousand Oak, CA: Sage; 2007.
-
- Bar-On R, Tranel D, Denburg NL, Bechara A. Exploring the neurological substrate of emotional and social intelligence. Brain. 2003;126:1790–1800. - PubMed
-
- Bates E, Wilson SM, Saygin AP, Dick F, Sereno MI, Knight RT, Dronkers NF. Voxel-based lesion-symptom mapping. Nat Neurosci. 2003;6:448–450. - PubMed
-
- Bornstein RA, Matarazzo JD. Wechsler VIQ versus PIQ differences in cerebral dysfunction: a literature review with emphasis on sex differences. J Clin Neuropsychol. 1982;4:319–334. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

