Mechanism for sortase localization and the role of sortase localization in efficient pilus assembly in Enterococcus faecalis
- PMID: 19286802
- PMCID: PMC2687161
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01837-08
Mechanism for sortase localization and the role of sortase localization in efficient pilus assembly in Enterococcus faecalis
Abstract
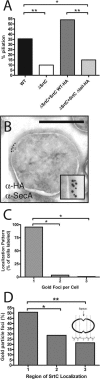
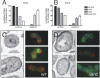
Pathogenic streptococci and enterococci primarily rely on the conserved secretory (Sec) pathway for the translocation and secretion of virulence factors out of the cell. Since many secreted virulence factors in gram-positive organisms are subsequently attached to the bacterial cell surface via sortase enzymes, we sought to investigate the spatial relationship between secretion and cell wall attachment in Enterococcus faecalis. We discovered that sortase A (SrtA) and sortase C (SrtC) are colocalized with SecA at single foci in the enterococcus. The SrtA-processed substrate aggregation substance accumulated in single foci when SrtA was deleted, implying a single site of secretion for these proteins. Furthermore, in the absence of the pilus-polymerizing SrtC, pilin subunits also accumulate in single foci. Proteins that localized to single foci in E. faecalis were found to share a positively charged domain flanking a transmembrane helix. Mutation or deletion of this domain in SrtC abolished both its retention at single foci and its function in efficient pilus assembly. We conclude that this positively charged domain can act as a localization retention signal for the focal compartmentalization of membrane proteins.
Figures

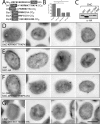
References
-
- Campo, N., H. Tjalsma, G. Buist, D. Stepniak, M. Meijer, M. Veenhuis, M. Westermann, J. P. Muller, S. Bron, J. Kok, O. P. Kuipers, and J. D. Jongbloed. 2004. Subcellular sites for bacterial protein export. Mol. Microbiol. 531583-1599. - PubMed
-
- Caparon, M. G., B. Poolman, and A. Podbielski. 2007. Streptococcal peptide trans-membrane transport, p. 327-358. In R. Hakenbeck and S. Chhatwal (ed.), Molecular biology of the streptococci. Horizon Scientific Press, Norwich, United Kingdom.
-
- Carlsson, F., M. Stalhammar-Carlemalm, K. Flardh, C. Sandin, E. Carlemalm, and G. Lindahl. 2006. Signal sequence directs localized secretion of bacterial surface proteins. Nature 442943-946. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

