Cognition and mood in Parkinson's disease in subthalamic nucleus versus globus pallidus interna deep brain stimulation: the COMPARE trial
- PMID: 19288469
- PMCID: PMC2692580
- DOI: 10.1002/ana.21596
Cognition and mood in Parkinson's disease in subthalamic nucleus versus globus pallidus interna deep brain stimulation: the COMPARE trial
Abstract
Objective: Our aim was to compare in a prospective blinded study the cognitive and mood effects of subthalamic nucleus (STN) vs. globus pallidus interna (GPi) deep brain stimulation (DBS) in Parkinson disease.
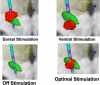
Methods: Fifty-two subjects were randomized to unilateral STN or GPi DBS. The co-primary outcome measures were the Visual Analog Mood Scale, and verbal fluency (semantic and letter) at 7 months post-DBS in the optimal setting compared to pre-DBS. At 7 months post-DBS, subjects were tested in four randomized/counterbalanced conditions (optimal, ventral, dorsal, and off DBS).
Results: Forty-five subjects (23 GPi, 22 STN) completed the protocol. The study revealed no difference between STN and GPi DBS in the change of co-primary mood and cognitive outcomes pre- to post-DBS in the optimal setting (Hotelling's T(2) test: p = 0.16 and 0.08 respectively). Subjects in both targets were less "happy", less "energetic" and more "confused" when stimulated ventrally. Comparison of the other 3 DBS conditions to pre-DBS showed a larger deterioration of letter verbal fluency in STN, especially when off DBS. There was no difference in UPDRS motor improvement between targets.
Interpretation: There were no significant differences in the co-primary outcome measures (mood and cognition) between STN and GPi in the optimal DBS state. Adverse mood effects occurred ventrally in both targets. A worsening of letter verbal fluency was seen in STN. The persistence of deterioration in verbal fluency in the off STN DBS state was suggestive of a surgical rather than a stimulation-induced effect. Similar motor improvement were observed with both STN and GPi DBS.
Figures
References
-
- Okun MS, Foote KD. Subthalamic nucleus vs globus pallidus interna deep brain stimulation, the rematch: will pallidal deep brain stimulation make a triumphant return? Arch Neurol. 2005;62:533–536. - PubMed
-
- Pahwa R, Factor SA, Lyons KE, et al. Practice Parameter: treatment of Parkinson disease with motor fluctuations and dyskinesia (an evidence-based review): report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology. 2006;66:983–995. - PubMed
-
- Deep-brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus or the pars interna of the globus pallidus in Parkinson's disease. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:956–963. - PubMed
-
- Weaver F, Follett K, Hur K, et al. Deep brain stimulation in Parkinson disease: a metaanalysis of patient outcomes. J Neurosurg. 2005;103:956–967. - PubMed
-
- Anderson VC, Burchiel KJ, Hogarth P, et al. Pallidal vs subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation in Parkinson disease. Arch Neurol. 2005;62:554–560. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

