Defective co-activator recruitment in osteoclasts from microphthalmia-oak ridge mutant mice
- PMID: 19288495
- PMCID: PMC2852098
- DOI: 10.1002/jcp.21755
Defective co-activator recruitment in osteoclasts from microphthalmia-oak ridge mutant mice
Abstract
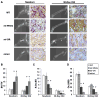
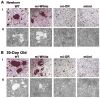
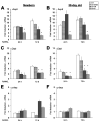
The three basic DNA-binding domain mutations of the microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (Mitf), Mitf(mi/mi), Mitf(or/or), and Mitf(wh/wh) affect osteoclast differentiation with variable penetrance while completely impairing melanocyte development. Mitf(or/or) mice exhibit osteopetrosis that improves with age and their osteoclasts form functional multinuclear osteoclasts, raising the question as to why the Mitf(or/or) mutation results in osteopetrosis. Here we show that Mitf(or/or) osteoclasts express normal levels of acid phosphatase 5 (Acp5) mRNA and significantly lower levels of Cathepsin K (Ctsk) mRNA during receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B (NFkappaB) ligand (RANKL)-mediated differentiation. Studies using chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) analysis indicate that low levels of Mitf(or/or) protein are recruited to the Ctsk promoter. However, enrichment of Mitf-transcriptional co-activators PU.1 and Brahma-related gene 1 (Brg1) are severely impaired at the Ctsk promoter of Mitf(or/or) osteoclast precursors, indicating that defective recruitment of co-activators by the mutant Mitf(or/or) results in impaired Ctsk expression in osteoclasts. Cathepsin K may thus represent a unique class of Mitf-regulated osteoclast-specific genes that are important for osteoclast function.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Eos, MITF, and PU.1 recruit corepressors to osteoclast-specific genes in committed myeloid progenitors.Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Jun;27(11):4018-27. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01839-06. Epub 2007 Apr 2. Mol Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17403896 Free PMC article.
-
The multifunctional protein fused in sarcoma (FUS) is a coactivator of microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF).J Biol Chem. 2014 Jan 3;289(1):326-34. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.493874. Epub 2013 Nov 20. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24257758 Free PMC article.
-
MITF and PU.1 recruit p38 MAPK and NFATc1 to target genes during osteoclast differentiation.J Biol Chem. 2007 May 25;282(21):15921-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M609723200. Epub 2007 Apr 2. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17403683
-
Mitf and Tfe3: members of a b-HLH-ZIP transcription factor family essential for osteoclast development and function.Bone. 2004 Apr;34(4):689-96. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2003.08.014. Bone. 2004. PMID: 15050900 Review.
-
Microphthalmia-associated transcription factor in the Wnt signaling pathway.Pigment Cell Res. 2003 Jun;16(3):261-5. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0749.2003.00039.x. Pigment Cell Res. 2003. PMID: 12753399 Review.
Cited by
-
The Unique Mechanisms of Cellular Proliferation, Migration and Apoptosis are Regulated through Oocyte Maturational Development-A Complete Transcriptomic and Histochemical Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Dec 26;20(1):84. doi: 10.3390/ijms20010084. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30587792 Free PMC article.
-
Failure to Target RANKL Signaling Through p38-MAPK Results in Defective Osteoclastogenesis in the Microphthalmia Cloudy-Eyed Mutant.J Cell Physiol. 2016 Mar;231(3):630-40. doi: 10.1002/jcp.25108. J Cell Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26218069 Free PMC article.
-
The Microphthalmia-Associated Transcription Factor (MITF) and Its Role in the Structure and Function of the Eye.Genes (Basel). 2024 Sep 27;15(10):1258. doi: 10.3390/genes15101258. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39457382 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Disruption of the transcription factor RBP-J results in osteopenia attributable to attenuated osteoclast differentiation.Mol Biol Rep. 2013 Mar;40(3):2097-105. doi: 10.1007/s11033-012-2268-6. Epub 2012 Dec 7. Mol Biol Rep. 2013. PMID: 23224519
-
MITF and PU.1 inhibit adipogenesis of ovine primary preadipocytes by restraining C/EBPβ.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2017 Jan 17;22:2. doi: 10.1186/s11658-016-0032-y. eCollection 2017. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2017. PMID: 28536633 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Angel NZ, Walsh N, Forwood MR, Ostrowski MC, Cassady AI, Hume DA. Transgenic mice overexpressing tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase exhibit an increased rate of bone turnover. J Bone Miner Res. 2000;15(1):103–110. - PubMed
-
- Boyce BF, Yao Z, Zhang Q, Guo R, Lu Y, Schwarz EM, Xing L. New roles for osteoclasts in bone. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 2007;1116:245–254. - PubMed
-
- Gowen M, Lazner F, Dodds R, Kapadia R, Feild J, Tavaria M, Bertoncello I, Drake F, Zavarselk S, Tellis I, Hertzog P, Debouck C, Kola I. Cathepsin K knockout mice develop osteopetrosis due to a deficit in matrix degradation but not demineralization. J Bone Miner Res. 1999;14(10):1654–1663. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

