Trophoblast stem cell maintenance by fibroblast growth factor 4 requires MEKK4 activation of Jun N-terminal kinase
- PMID: 19289495
- PMCID: PMC2682043
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01391-08
Trophoblast stem cell maintenance by fibroblast growth factor 4 requires MEKK4 activation of Jun N-terminal kinase
Abstract
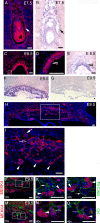
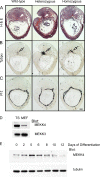
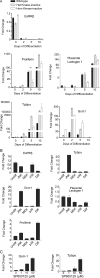
Trophoblast differentiation during placentation involves an epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) with loss of E-cadherin and gain of trophoblast invasiveness. Mice harboring a point mutation that renders inactive the mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase MEKK4 exhibit dysregulated placental development with increased trophoblast invasion. Isolated MEKK4 kinase-inactive trophoblast stem (TS) cells cultured under undifferentiating, self-renewing conditions in the presence of fibroblast growth factor 4 (FGF4) display increased expression of Slug, Twist, and matrix metalloproteinase 2 (MMP2), loss of E-cadherin, and hyperinvasion of extracellular matrix, each a hallmark of EMT. MEKK4 kinase-inactive TS cells show a preferential differentiation to Tpbp alpha- and Gcm1-positive trophoblasts, which are indicative of spongiotrophoblast and syncytiotrophoblast differentiation, respectively. FGF4-stimulated Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and p38 activity is markedly reduced in MEKK4 kinase-inactive TS cells. Chemical inhibition of JNK in wild-type TS cells induced a similar EMT response as loss of MEKK4 kinase activity, including inhibition of E-cadherin expression and increased expression of Slug, MMP2, Tpbp alpha, and Gcm1. Chromatin immunoprecipitation analyses revealed changes in AP-1 composition with increased Fra-2 and decreased Fra-1 and JunB binding to the regulatory regions of Gcm1 and MMP2 genes in MEKK4 kinase-inactive TS cells. Our results define MEKK4 as a signaling hub for FGF4 activation of JNK that is required for maintenance of TS cells in an undifferentiated state.
Figures





References
-
- Abell, A. N., D. A. Granger, and G. L. Johnson. 2007. MEKK4 stimulation of p38 and JNK activity is negatively regulated by GSK3β. J. Biol. Chem. 28230476-30484. - PubMed
-
- Abell, A. N., and G. L. Johnson. 2005. MEKK4 is an effector of the embryonic TRAF4 for JNK activation. J. Biol. Chem. 28035793-35796. - PubMed
-
- Abell, A. N., J. A. Rivera-Perez, B. D. Cuevas, M. T. Uhlik, S. Sather, N. L. Johnson, S. K. Minton, J. M. Lauder, A. M. Winter-Vann, K. Nakamura, T. Magnuson, R. R. Vaillancourt, L. E. Heasley, and G. L. Johnson. 2005. Ablation of MEKK4 kinase activity causes neurulation and skeletal patterning defects in the mouse embryo. Mol. Cell. Biol. 258948-8959. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Batlle, E., E. Sancho, C. Franci, D. Dominguez, M. Monfar, J. Baulida, and A. Garcia De Herreros. 2000. The transcription factor snail is a repressor of E-cadherin gene expression in epithelial tumour cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 284-89. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
