Dynamic integration of subplate neurons into the cortical barrel field circuitry during postnatal development in the Golli-tau-eGFP (GTE) mouse
- PMID: 19289548
- PMCID: PMC2689332
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2008.167767
Dynamic integration of subplate neurons into the cortical barrel field circuitry during postnatal development in the Golli-tau-eGFP (GTE) mouse
Abstract
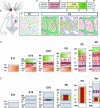
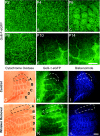
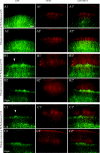
In the Golli-tau-eGFP (GTE) transgenic mouse the reporter gene expression is largely confined to the layer of subplate neurons (SPn), providing an opportunity to study their intracortical and extracortical projections. In this study, we examined the thalamic afferents and layer IV neuron patterning in relation to the SPn neurites in the developing barrel cortex in GTE mouse at ages embryonic day 17 (E17) to postnatal day 14 (P14). Serotonin transporter immunohistochemistry or cytochrome oxydase histochemistry was used to reveal thalamic afferent patterning. Bizbenzimide staining identified the developing cytoarchitecture in coronal and tangential sections of GTE brains. Enhanced green fluorescent protein (GFP)-labelled neurites and thalamic afferents were both initially diffusely present in layer IV but by P4-P6 both assumed the characteristic periphery-related pattern and became restricted to the barrel hollows. This pattern gradually changed and by P10 the GFP-labelled neurites largely accumulated at the layer IV-V boundary within the barrel septa whereas thalamic afferents remained in the hollows. To investigate whether this reorganisation is dependent on sensory input, the whiskers of row 'a' or 'c' were removed at P0 or P5 and the organisation of GFP-labelled neurites in the barrel cortex was examined at P6 or P10. In the contralateral region corresponding to row 'a' or 'c' the lack of hollow to septa rearrangement of the GFP-labelled neurites was observed after P0 row removal at P10 but not at P6. Our findings suggest a dynamic, sensory periphery-dependent integration of SPn neurites into the primary somatosensory cortex during the period of barrel formation.
Figures

References
-
- Allendoerfer KL, Shatz CJ. The subplate, a transient neocortical structure: its role in the development of connections between the thalamus and cortex. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1994;17:185–218. - PubMed
-
- Antonini A, Shatz CJ. Relation between putative transmitter phenotypes and connectivity of subplate neurons during cerebral cortical development. Eur J Neurosci. 1990;2:744–761. - PubMed
-
- Arber S. Subplate neurons: bridging the gap to function in the cortex. Trends Neurosci. 2004;27:111–113. - PubMed
-
- Aye L, Piñon MC, Hoerder A, Jacobs E, Campagnoni A, Molnár Z. Properties of layer 6a and subplate neurons in the Golli Tau eGFP (GTE) mouse. FENS Abstr. 2006;3:A196.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

