Prostaglandin mediates IL-23/IL-17-induced neutrophil migration in inflammation by inhibiting IL-12 and IFNgamma production
- PMID: 19289819
- PMCID: PMC2667068
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0812782106
Prostaglandin mediates IL-23/IL-17-induced neutrophil migration in inflammation by inhibiting IL-12 and IFNgamma production
Abstract
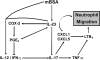
IL-23/IL-17-induced neutrophil recruitment plays a pivotal role in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). However, the mechanism of the neutrophil recruitment is obscure. Here we report that prostaglandin enhances the IL-23/IL-17-induced neutrophil migration in a murine model of RA by inhibiting IL-12 and IFN gamma production. Methylated BSA (mBSA) and IL-23-induced neutrophil migration was inhibited by anti-IL-23 and anti-IL-17 antibodies, COX inhibitors, IL-12, or IFNgamma but was enhanced by prostaglandin E(2) (PGE(2)). IL-23-induced IL-17 production was increased by PGE(2) and suppressed by COX-inhibition or IL-12. Furthermore, COX inhibition failed to reduce IL-23-induced neutrophil migration in IL-12- or IFNgamma-deficient mice. IL-17-induced neutrophil migration was not affected by COX inhibitors, IL-12, or IFNgamma but was inhibited by MK886 (a leukotriene synthesis inhibitor), anti-TNFalpha, anti-CXCL1, and anti-CXCL5 antibodies and by repertaxin (a CXCR1/2 antagonist). These treatments all inhibited mBSA- or IL-23-induced neutrophil migration. IL-17 induced neutrophil chemotaxis through a CXC chemokines-dependent pathway. Our results suggest that prostaglandin plays an important role in IL-23-induced neutrophil migration in arthritis by enhancing IL-17 synthesis and by inhibiting IL-12 and IFNgamma production. We thus provide a mechanism for the pathogenic role of the IL-23/IL-17 axis in RA and also suggest an additional mechanism of action for nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


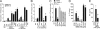
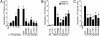
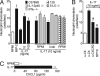
References
-
- Liew FY, McInnes IB. A fork in the pathway to inflammation and arthritis. Nat Med. 2005;11(6):601–602. - PubMed
-
- Wipke BT, Allen PM. Essential role of neutrophils in the initiation and progression of a murine model of rheumatoid arthritis. J Immunol. 2001;167(3):1601–1608. - PubMed
-
- Mohr W, Wessinghage D. The relationship between polymorphonuclear granulocytes and cartilage destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. Zeitschrift für Rheumatologie. 1978;37(3–4):81–86. - PubMed
-
- McIntyre KW, et al. Reduced incidence and severity of collagen-induced arthritis in interleukin-12-deficient mice. Eur J Immunol. 1996;26(12):2933–2938. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

