A conserved mechanism for control of human and mouse embryonic stem cell pluripotency and differentiation by shp2 tyrosine phosphatase
- PMID: 19290061
- PMCID: PMC2655646
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0004914
A conserved mechanism for control of human and mouse embryonic stem cell pluripotency and differentiation by shp2 tyrosine phosphatase
Abstract
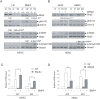
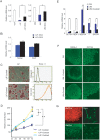
Recent studies have suggested distinctive biological properties and signaling mechanisms between human and mouse embryonic stem cells (hESCs and mESCs). Herein we report that Shp2, a protein tyrosine phosphatase with two SH2 domains, has a conserved role in orchestration of intracellular signaling cascades resulting in initiation of differentiation in both hESCs and mESCs. Homozygous deletion of Shp2 in mESCs inhibited differentiation into all three germ layers, and siRNA-mediated knockdown of Shp2 expression in hESCs led to a similar phenotype of impaired differentiation. A small molecule inhibitor of Shp2 enzyme suppressed both hESC and mESC differentiation capacity. Shp2 modulates Erk, Stat3 and Smad pathways in ES cells and, in particular, Shp2 regulates BMP4-Smad pathway bi-directionally in mESCs and hESCs. These results reveal a common signaling mechanism shared by human and mouse ESCs via Shp2 modulation of overlapping and divergent pathways.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Thomson JA, Itskovitz-Eldor J, Shapiro SS, Waknitz MA, Swiergiel JJ, et al. Embryonic stem cell lines derived from human blastocysts. Science. 1998;282:1145–1147. - PubMed
-
- Loh YH, Wu Q, Chew JL, Vega VB, Zhang W, et al. The Oct4 and Nanog transcription network regulates pluripotency in mouse embryonic stem cells. Nat Genet. 2006;38:431–440. - PubMed
-
- Sato N, Sanjuan IM, Heke M, Uchida M, Naef F, et al. Molecular signature of human embryonic stem cells and its comparison with the mouse. Dev Biol. 2003;260:404–413. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

