Changes in sonographic findings after treatment of patients with clonorchiasis in a heavy endemic area
- PMID: 19290087
- PMCID: PMC2655335
- DOI: 10.3347/kjp.2009.47.1.19
Changes in sonographic findings after treatment of patients with clonorchiasis in a heavy endemic area
Abstract
We measured changes in sonographic findings of patients with clonorchiasis after a treatment in a highly endemic area. A total of 347 residents showed positive stool results for Clonorchis sinensis eggs in a village in northeastern China, and were treated with praziquantel. Of them, 132 patients underwent abdominal sonography both before and 1 year after treatment, and the changes in sonographic findings of 83 cured subjects were compared. Diffuse dilatation of intrahepatic bile ducts (DDIHD) was found in 82 patients (98.2%) before and 80 (96.4%) after treatment, which was improved in 3, aggravated in 1, and unchanged in 79 patients. Increased periductal echogenicity (IPDE) was observed in 42 patients (50.6%) before and 45 (54.2%) after treatment, which was improved in 5, aggravated in 8, and unchanged in 70 patients. Floating echogenic foci in the gallbladder (FEFGB) was detected in 32 patients (38.6%) before and 17 (20.5%) after treatment, which was improved in 20, aggravated in 5, and unchanged in 58 patients. Improvement of FEFGB only was statistically significantly (P = 0.004). The present results confirm that DDIHD and IPDE persist but FEFGB decreases significantly at 1 year after treatment. In a heavy endemic area, the sonographic finding of FEFGB may suggest active clonorchiasis 1 year after treatment.
Keywords: Clonorchis sinensis; abdominal sonography; dilatation of intrahepatic bile ducts; floating echogenic foci in the gallbladder; periductal echogenicity; praziquantel.
Figures
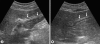

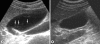
References
-
- Rim HJ. Clonorchiasis: an update. J Helminthol. 2005;79:269–281. - PubMed
-
- Lee JH, Rim HJ, Sell S. Heterogeneity of the "oval-cell" response in the hamster liver during cholangiocarcinogenesis following Clonorchis sinensis infection and dimethylnitrosamine treatment. J Hepatol. 1997;26:1313–1323. - PubMed
-
- Choi D, Lim JH, Lee KT, Lee JK, Choi SH, Heo JS, Jang KT, Lee NY, Kim S, Hong ST. Cholangiocarcinoma and Clonorchis sinensis infection: a case-control study in Korea. J Hepatol. 2006;44:1066–1073. - PubMed
-
- Lim MK, Ju YH, Franceschi S, Oh JK, Kong HJ, Hwang SS, Park SK, Cho SI, Sohn WM, Kimg DI, Yoo KY, Hong ST, Shin HR. Clonorchis sinensis infection and increasing risk of cholangiocarcinoma in the Republic of Korea. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2006;75:93–96. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

