CARMA1-mediated NF-kappaB and JNK activation in lymphocytes
- PMID: 19290929
- PMCID: PMC2878635
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2008.00749.x
CARMA1-mediated NF-kappaB and JNK activation in lymphocytes
Abstract
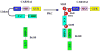
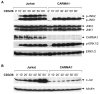
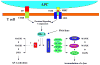
Activation of transcription factor nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) and Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) play the pivotal roles in regulation of lymphocyte activation and proliferation. Deregulation of these signaling pathways leads to inappropriate immune response and contributes to the development of leukemia/lymphoma. The scaffold protein CARMA1 [caspase-recruitment domain (CARD) membrane-associated guanylate kinase (MAGUK) protein 1] has a central role in regulation of NF-kappaB and the JNK2/c-Jun complex in both B and T lymphocytes. During last several years, tremendous work has been done to reveal the mechanism by which CARMA1 and its signaling partners, B cell CLL-lymphoma 10 and mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue 1, are activated and mediate NF-kappaB and JNK activation. In this review, we summarize our findings in revealing the roles of CARMA1 in the NF-kappaB and JNK signaling pathways in the context of recent advances in this field.
Figures



References
-
- Samelson LE. Signal transduction mediated by the T cell antigen receptor: the role of adapter proteins. Annu Rev Immunol. 2002;20:371–394. - PubMed
-
- Clements JL, Boerth NJ, Lee JR, Koretzky GA. Integration of T cell receptor-dependent signaling pathways by adapter proteins. Annu Rev Immunol. 1999;17:89–108. - PubMed
-
- Schulze-Luehrmann J, Ghosh S. Antigen-receptor signaling to nuclear factor kappa B. Immunity. 2006;25:701–715. - PubMed
-
- Karin M, Lin A. NF-kappaB at the crossroads of life and death. Nat Immunol. 2002;3:221–227. - PubMed
-
- Karin M, Ben-Neriah Y. Phosphorylation meets ubiquitination: the control of NF-[kappa]B activity. Annu Rev Immunol. 2000;18:621–663. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

