Synchronous GABA-receptor-dependent potentials in limbic areas of the in-vitro isolated adult guinea pig brain
- PMID: 19291222
- PMCID: PMC4873282
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2009.06672.x
Synchronous GABA-receptor-dependent potentials in limbic areas of the in-vitro isolated adult guinea pig brain
Abstract
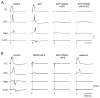
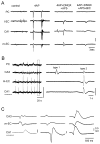
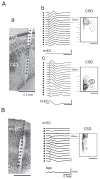
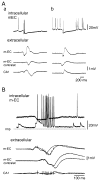
Epileptiform discharges are known to reflect the hypersynchronous glutamatergic activation of cortical neurons. However, experimental evidence has revealed that epileptiform synchronization is also contributed to by population events mediated by GABA(A) receptors. Here, we analysed the spatial distribution of GABA(A)-receptor-dependent interictal events in the hippocampal/parahippocampal region of the adult guinea pig brain isolated in vitro. We found that arterial perfusion of this preparation with 4-aminopyridine caused the appearance of glutamatergic-independent interictal potentials that were reversibly abolished by GABA(A) receptor antagonism. Laminar profiles and current source density analysis performed in different limbic areas demonstrated that these GABA(A)-receptor-mediated events were independently generated in different areas of the hippocampal/parahippocampal formation (most often in the medial entorhinal cortex) and propagated between interconnected limbic structures of both hemispheres. Finally, intracellular recordings from principal neurons of the medial entorhinal cortex demonstrated that the GABAergic field potential correlated to inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (membrane potential reversal, -68.12 +/- 8.01 mV, n = 5) that were interrupted by ectopic spiking. Our findings demonstrate that, in an acute seizure model developed in the adult guinea pig brain, hypersynchronous GABA(A)-receptor-mediated interictal events are generated from independent sources and propagate within limbic cortices in the absence of excitatory synaptic transmission. As spared or enhanced inhibition was reported in models of epilepsy, our data may support a role of GABA-mediated signaling in ictogenesis and epileptogenesis.
Figures

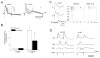

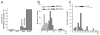
Similar articles
-
Independent epileptiform discharge patterns in the olfactory and limbic areas of the in vitro isolated Guinea pig brain during 4-aminopyridine treatment.J Neurophysiol. 2010 May;103(5):2728-36. doi: 10.1152/jn.00862.2009. Epub 2010 Mar 10. J Neurophysiol. 2010. PMID: 20220076 Free PMC article.
-
GABAergic synchronization in the limbic system and its role in the generation of epileptiform activity.Prog Neurobiol. 2011 Oct;95(2):104-32. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2011.07.003. Epub 2011 Jul 23. Prog Neurobiol. 2011. PMID: 21802488 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synchronous inhibitory potentials precede seizure-like events in acute models of focal limbic seizures.J Neurosci. 2015 Feb 18;35(7):3048-55. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3692-14.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25698742 Free PMC article.
-
Propagation dynamics of epileptiform activity acutely induced by bicuculline in the hippocampal-parahippocampal region of the isolated Guinea pig brain.Epilepsia. 2005 Dec;46(12):1914-25. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1167.2005.00342.x. Epilepsia. 2005. PMID: 16393157
-
Network and pharmacological mechanisms leading to epileptiform synchronization in the limbic system in vitro.Prog Neurobiol. 2002 Oct;68(3):167-207. doi: 10.1016/s0301-0082(02)00077-1. Prog Neurobiol. 2002. PMID: 12450487 Review.
Cited by
-
Independent epileptiform discharge patterns in the olfactory and limbic areas of the in vitro isolated Guinea pig brain during 4-aminopyridine treatment.J Neurophysiol. 2010 May;103(5):2728-36. doi: 10.1152/jn.00862.2009. Epub 2010 Mar 10. J Neurophysiol. 2010. PMID: 20220076 Free PMC article.
-
GABAergic synchronization in the limbic system and its role in the generation of epileptiform activity.Prog Neurobiol. 2011 Oct;95(2):104-32. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2011.07.003. Epub 2011 Jul 23. Prog Neurobiol. 2011. PMID: 21802488 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Involvement of GABAergic Interneuron Subtypes in 4-Aminopyridine-Induced Seizure-Like Events in Mouse Entorhinal Cortex in Vitro.J Neurosci. 2023 Mar 15;43(11):1987-2001. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1190-22.2023. Epub 2023 Feb 21. J Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36810229 Free PMC article.
-
Hilar somatostatin interneurons contribute to synchronized GABA activity in an in vitro epilepsy model.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 21;9(1):e86250. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0086250. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24465989 Free PMC article.
-
Synchronous inhibitory potentials precede seizure-like events in acute models of focal limbic seizures.J Neurosci. 2015 Feb 18;35(7):3048-55. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3692-14.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25698742 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aram JA, Lodge D. Epileptiform activity induced by alkalosis in rat neocortical slices: block by antagonists of N-methyl-D-aspartate. Neurosci Lett. 1987;83:345–350. - PubMed
-
- Aram JA, Michelson HB, Wong RKS. Synchronized GABAergic IPSPs recorded in the neocortex after blockade of synaptic transmission mediated by excitatory amino acids. J Neurophysiol. 1991;65:1034–1041. - PubMed
-
- Avoli M, Mattia D, Siniscalchi A, Perreault P, Tomaiuolo F. Pharmacology and electrophysiology of a synchronous GABA-mediated potential in the human neocortex. Neuroscience. 1994;62:655–666. - PubMed
-
- Avoli M, Methot M, Kawasaki H. GABA-dependent generation of ectopic action potentials in the rat hippocampus. Eur J Neurosci. 1998;10:2714–2722. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

